This introduces a tiny alternative to our stdlib, that can be used for testing the interpreter. There are 2 main advantages of such a solution:
1. Performance: on my machine, `runtime-with-intstruments/test` drops from 146s to 65s, while `runtime/test` drops from 165s to 51s. >6 mins total becoming <2 mins total is awesome. This alone means I'll drink less coffee in these breaks and will be healthier.
2. Better separation of concepts – currently working on a feature that breaks _all_ enso code. The dependency of interpreter tests on the stdlib means I have no means of incremental testing – ALL of stdlib must compile. This is horrible, rendered my work impossible, and resulted in this PR.
New plan to [fix the `sbt` build](https://www.pivotaltracker.com/n/projects/2539304/stories/182209126) and its annoying:
```
log.error(
"Truffle Instrumentation is not up to date, " +
"which will lead to runtime errors\n" +
"Fixes have been applied to ensure consistent Instrumentation state, " +
"but compilation has to be triggered again.\n" +
"Please re-run the previous command.\n" +
"(If this for some reason fails, " +
s"please do a clean build of the $projectName project)"
)
```
When it is hard to fix `sbt` incremental compilation, let's restructure our project sources so that each `@TruffleInstrument` and `@TruffleLanguage` registration is in individual compilation unit. Each such unit is either going to be compiled or not going to be compiled as a batch - that will eliminate the `sbt` incremental compilation issues without addressing them in `sbt` itself.
fa2cf6a33ec4a5b2e3370e1b22c2b5f712286a75 is the first step - it introduces `IdExecutionService` and moves all the `IdExecutionInstrument` API up to that interface. The rest of the `runtime` project then depends only on `IdExecutionService`. Such refactoring allows us to move the `IdExecutionInstrument` out of `runtime` project into independent compilation unit.
Auto-generate all builtin methods for builtin `File` type from method signatures.
Similarly, for `ManagedResource` and `Warning`.
Additionally, support for specializations for overloaded and non-overloaded methods is added.
Coverage can be tracked by the number of hard-coded builtin classes that are now deleted.
## Important notes
Notice how `type File` now lacks `prim_file` field and we were able to get rid off all of those
propagating method calls without writing a single builtin node class.
Similarly `ManagedResource` and `Warning` are now builtins and `Prim_Warnings` stub is now gone.
Drop `Core` implementation (replacement for IR) as it (sadly) looks increasingly
unlikely this effort will be continued. Also, it heavily relies
on implicits which increases some compilation time (~1sec from `clean`)
Related to https://www.pivotaltracker.com/story/show/182359029
@radeusgd discovered that no formatting was being applied to std-bits projects.
This was caused by the fact that `enso` project didn't aggregate them. Compilation and
packaging still worked because one relied on the output of some tasks but
```
sbt> javafmtAll
```
didn't apply it to `std-bits`.
# Important Notes
Apart from `build.sbt` no manual changes were made.
This is the 2nd part of DSL improvements that allow us to generate a lot of
builtins-related boilerplate code.
- [x] generate multiple method nodes for methods/constructors with varargs
- [x] expanded processing to allow for @Builtin to be added to classes and
and generate @BuiltinType classes
- [x] generate code that wraps exceptions to panic via `wrapException`
annotation element (see @Builtin.WrapException`
Also rewrote @Builtin annotations to be more structured and introduced some nesting, such as
@Builtin.Method or @Builtin.WrapException.
This is part of incremental work and a follow up on https://github.com/enso-org/enso/pull/3444.
# Important Notes
Notice the number of boilerplate classes removed to see the impact.
For now only applied to `Array` but should be applicable to other types.
Promoted `with`, `take`, `finalize` to be methods of Managed_Resource
rather than static methods always taking `resource`, for consistency
reasons.
This required function dispatch boilerplate, similarly to `Ref`.
In future iterations we will address this boilerplate code.
Related to https://www.pivotaltracker.com/story/show/182212217
The change promotes static methods of `Ref`, `get` and `put`, to be
methods of `Ref` type.
The change also removes `Ref` module from the default namespace.
Had to mostly c&p functional dispatch for now, in order for the methods
to be found. Will auto-generate that code as part of builtins system.
Related to https://www.pivotaltracker.com/story/show/182138899
Before, when running Enso with `-ea`, some assertions were broken and the interpreter would not start.
This PR fixes two very minor bugs that were the cause of this - now we can successfully run Enso with `-ea`, to test that any assertions in Truffle or in our own libraries are indeed satisfied.
Additionally, this PR adds a setting to SBT that ensures that IntelliJ uses the right language level (Java 17) for our projects.
A low-hanging fruit where we can automate the generation of many
@BuiltinMethod nodes simply from the runtime's methods signatures.
This change introduces another annotation, @Builtin, to distinguish from
@BuiltinType and @BuiltinMethod processing. @Builtin processing will
always be the first stage of processing and its output will be fed to
the latter.
Note that the return type of Array.length() is changed from `int` to
`long` because we probably don't want to add a ton of specializations
for the former (see comparator nodes for details) and it is fine to cast
it in a small number of places.
Progress is visible in the number of deleted hardcoded classes.
This is an incremental step towards #181499077.
# Important Notes
This process does not attempt to cover all cases. Not yet, at least.
We only handle simple methods and constructors (see removed `Array` boilerplate methods).
In order to analyse why the `runner.jar` is slow to start, let's _"self sample"_ it using the [sampler library](https://bits.netbeans.org/dev/javadoc/org-netbeans-modules-sampler/org/netbeans/modules/sampler/Sampler.html). As soon as the `Main.main` is launched, the sampling starts and once the server is up, it writes its data into `/tmp/language-server.npss`.
Open the `/tmp/language-server.npss` with [VisualVM](https://visualvm.github.io) - you should have one copy in your
GraalVM `bin/jvisualvm` directory and there has to be a GraalVM to run Enso.
#### Changelog
- add: the `MethodsSampler` that gathers information in `.npss` format
- add: `--profiling` flag that enables the sampler
- add: language server processes the updates in batches
Finally this pull request proposes `--inspect` option to allow [debugging of `.enso`](e948f2535f/docs/debugger/README.md) in Chrome Developer Tools:
```bash
enso$ ./built-distribution/enso-engine-0.0.0-dev-linux-amd64/enso-0.0.0-dev/bin/enso --inspect --run ./test/Tests/src/Data/Numbers_Spec.enso
Debugger listening on ws://127.0.0.1:9229/Wugyrg9Nm4OUL9YhzdcElmLft71ayZW3LMUPCdPyNAY
For help, see: https://www.graalvm.org/tools/chrome-debugger
E.g. in Chrome open: devtools://devtools/bundled/js_app.html?ws=127.0.0.1:9229/Wugyrg9Nm4OUL9YhzdcElmLft71ayZW3LMUPCdPyNAY
```
copy the printed URL into chrome browser and you should see:
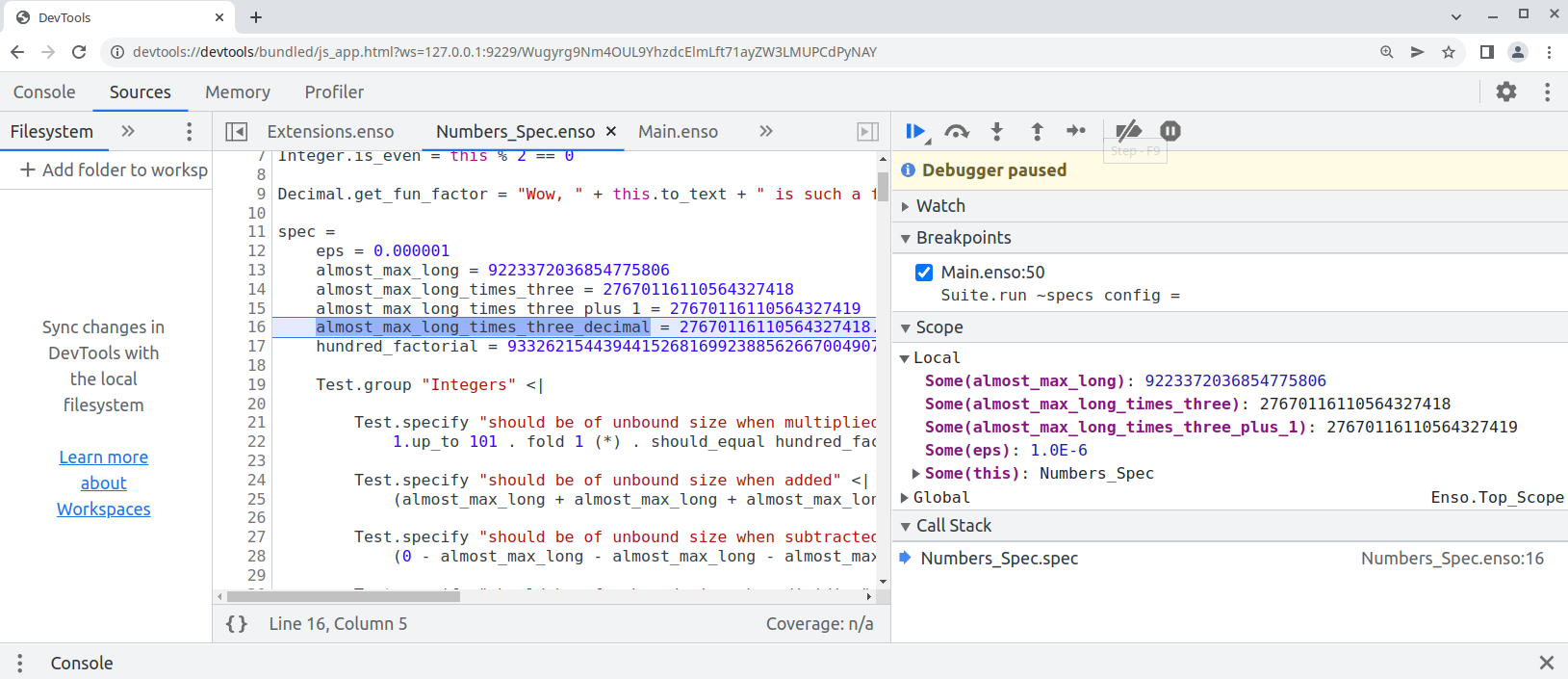
One can also debug the `.enso` files in NetBeans or [VS Code with Apache Language Server extension](https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/NETBEANS/Apache+NetBeans+Extension+for+Visual+Studio+Code) just pass in special JVM arguments:
```bash
enso$ JAVA_OPTS=-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,address=8000 ./built-distribution/enso-engine-0.0.0-dev-linux-amd64/enso-0.0.0-dev/bin/enso --run ./test/Tests/src/Data/Numbers_Spec.enso
Listening for transport dt_socket at address: 8000
```
and then _Debug/Attach Debugger_. Once connected choose the _Toggle Pause in GraalVM Script_ button in the toolbar (the "G" button):
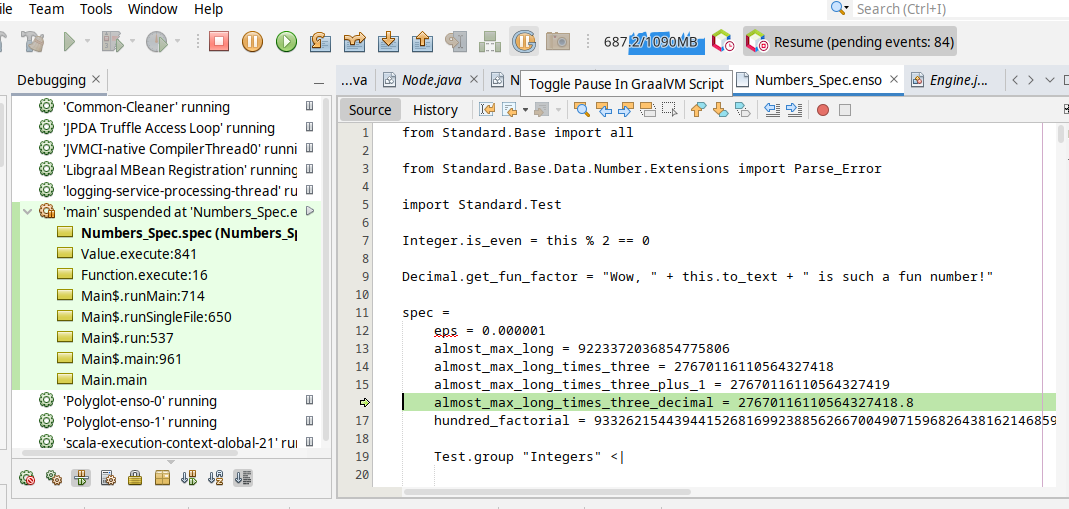
and your execution shall stop on the next `.enso` line of code. This mode allows to debug both - the Enso code as well as Java code.
Originally started as an attempt to write test in Java:
* test written in Java
* support for JUnit in `build.sbt`
* compile Java with `-g` - so it can be debugged
* Implementation of `StatementNode` - only gets created when `materialize` request gets to `BlockNode`
Debug is not imported by default (let me know if it should be?)
# Important Notes
When Debug was part of Builtins.enso everything was imported. Let me know if the new setup is not as expected.
This PR replaces hard-coded `@Builtin_Method` and `@Builtin_Type` nodes in Builtins with an automated solution
that a) collects metadata from such annotations b) generates `BuiltinTypes` c) registers builtin methods with corresponding
constructors.
The main differences are:
1) The owner of the builtin method does not necessarily have to be a builtin type
2) You can now mix regular methods and builtin ones in stdlib
3) No need to keep track of builtin methods and types in various places and register them by hand (a source of many typos or omissions as it found during the process of this PR)
Related to #181497846
Benchmarks also execute within the margin of error.
### Important Notes
The PR got a bit large over time as I was moving various builtin types and finding various corner cases.
Most of the changes however are rather simple c&p from Builtins.enso to the corresponding stdlib module.
Here is the list of the most crucial updates:
- `engine/runtime/src/main/java/org/enso/interpreter/runtime/builtin/Builtins.java` - the core of the changes. We no longer register individual builtin constructors and their methods by hand. Instead, the information about those is read from 2 metadata files generated by annotation processors. When the builtin method is encountered in stdlib, we do not ignore the method. Instead we lookup it up in the list of registered functions (see `getBuiltinFunction` and `IrToTruffle`)
- `engine/runtime/src/main/java/org/enso/interpreter/runtime/callable/atom/AtomConstructor.java` has now information whether it corresponds to the builtin type or not.
- `engine/runtime/src/main/scala/org/enso/compiler/codegen/RuntimeStubsGenerator.scala` - when runtime stubs generator encounters a builtin type, based on the @Builtin_Type annotation, it looks up an existing constructor for it and registers it in the provided scope, rather than creating a new one. The scope of the constructor is also changed to the one coming from stdlib, while ensuring that synthetic methods (for fields) also get assigned correctly
- `engine/runtime/src/main/scala/org/enso/compiler/codegen/IrToTruffle.scala` - when a builtin method is encountered in stdlib we don't generate a new function node for it, instead we look it up in the list of registered builtin methods. Note that Integer and Number present a bit of a challenge because they list a whole bunch of methods that don't have a corresponding method (instead delegating to small/big integer implementations).
During the translation new atom constructors get initialized but we don't want to do it for builtins which have gone through the process earlier, hence the exception
- `lib/scala/interpreter-dsl/src/main/java/org/enso/interpreter/dsl/MethodProcessor.java` - @Builtin_Method processor not only generates the actual code fpr nodes but also collects and writes the info about them (name, class, params) to a metadata file that is read during builtins initialization
- `lib/scala/interpreter-dsl/src/main/java/org/enso/interpreter/dsl/MethodProcessor.java` - @Builtin_Method processor no longer generates only (root) nodes but also collects and writes the info about them (name, class, params) to a metadata file that is read during builtins initialization
- `lib/scala/interpreter-dsl/src/main/java/org/enso/interpreter/dsl/TypeProcessor.java` - Similar to MethodProcessor but handles @Builtin_Type annotations. It doesn't, **yet**, generate any builtin objects. It also collects the names, as present in stdlib, if any, so that we can generate the names automatically (see generated `types/ConstantsGen.java`)
- `engine/runtime/src/main/java/org/enso/interpreter/node/expression/builtin` - various classes annotated with @BuiltinType to ensure that the atom constructor is always properly registered for the builitn. Note that in order to support types fields in those, annotation takes optional `params` parameter (comma separated).
- `engine/runtime/src/bench/scala/org/enso/interpreter/bench/fixtures/semantic/AtomFixtures.scala` - drop manual creation of test list which seemed to be a relict of the old design
A draft of simple changes to the compiler to expose sum type information. Doesn't break the stdlib & at the same time allows for dropdowns. This is still broken, for example it doesn't handle exporting/importing types, only ones defined in the same module as the signature. Still, seems like a step in the right direction – please provide feedback.
# Important Notes
I've decided to make the variant info part of the type, not the argument – it is a property of the type logically.
Also, I've pushed it as far as I'm comfortable – i.e. to the `SuggestionHandler` – I have no idea if this is enough to show in IDE? cc @4e6
Most of the functions in the standard library aren't gonna be invoked during particular program execution. It makes no sense to build their Truffle AST for the functions that are not executing. Let's delay the construction of the tree until a function is first executed.
Changelog:
- fix: `search/completion` request with the position parameter.
- fix: `refactoring/renameProject` request. Previously it did not take into account the library namespace (e.g. `local.`)
[ci no changelog needed]
# Important Notes
The REPL used to use some builtin Java text representation leading to outputs like this:
```
> [1,2,3]
>>> Vector [1, 2, 3]
> 'a,b,c'.split ','
>>> Vector JavaObject[[Ljava.lang.String;@131c0b6f (java.lang.String[])]
```
This PR makes it use `to_text` (if available, otherwise falling back to regular `toString`). This way we get outputs like this:
```
> [1,2,3]
>>> [1, 2, 3]
> 'a,b,c'.split ','
>>> ['a', 'b', 'c']
```
Result of automatic formatting with `scalafmtAll` and `javafmtAll`.
Prerequisite for https://github.com/enso-org/enso/pull/3394
### Important Notes
This touches a lot of files and might conflict with existing PRs that are in progress. If that's the case, just run
`scalafmtAll` and `javafmtAll` after merge and everything should be in order since formatters should be deterministic.
Changelog:
- add: component groups to package descriptions
- add: `executionContext/getComponentGroups` method that returns component groups of libraries that are currently loaded
- doc: cleanup unimplemented undo/redo commands
- refactor: internal component groups datatype
PR adds a monitor that handles messages between the language server and the runtime and dumps them as a CSV file `/tmp/enso-api-events-*********.csv`
```
UTC timestamp,Direction,Request Id,Message class
```
# Important Notes
⚠️ Monitor is enabled when the log level is set to trace. You should pass `-vv` (very verbose) option to the backend when starting IDE
```
enso -- -vv
```
Implements https://www.pivotaltracker.com/story/show/181805693 and finishes the basic set of features of the Aggregate component.
Still not all aggregations are supported everywhere, because for example SQLite has quite limited support for aggregations. Currently the workaround is to bring the table into memory (if possible) and perform the computation locally. Later on, we may add more complex generator features to emulate the missing aggregations with complex sub-queries.
Implements infrastructure for new aggregations in the Database. It comes with only some basic aggregations and limited error-handling. More aggregations and problem handling will be added in subsequent PRs.
# Important Notes
This introduces basic aggregations using our existing codegen and sets-up our testing infrastructure to be able to use the same aggregate tests as in-memory backend for the database backends.
Many aggregations are not yet implemented - they will be added in subsequent tasks.
There are some TODOs left - they will be addressed in the next tasks.