# Haskell IDE Engine (HIE)
 [![License BSD3][badge-license]][license]
[![CircleCI][badge-circleci]][circleci]
[![AppVeyor][badge-appveyor]][appveyor]
[](https://www.codetriage.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine)
[badge-license]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-BSD3-green.svg?dummy
[license]: https://github.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/blob/master/LICENSE
[badge-circleci]: https://img.shields.io/circleci/project/github/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/master.svg
[circleci]: https://circleci.com/gh/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/
[badge-appveyor]: https://ci.appveyor.com/api/projects/status/6hit7mxvgdrao3q0?svg=true
[appveyor]: https://ci.appveyor.com/project/Bubba/haskell-ide-engine-74xec
This project aims to be __the universal interface__ to __a growing number of Haskell tools__, providing a __full-featured and easy to query backend__ for editors and IDEs that require Haskell-specific functionality.
__We are currently focusing on using the [Language Server Protocol](https://github.com/Microsoft/language-server-protocol/blob/master/protocol.md) as the interface via which
we talk to clients.__
- [Haskell IDE Engine (HIE)](#haskell-ide-engine-hie)
- [Features](#features)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Installation with Nix](#installation-with-nix)
- [Installation on ArchLinux](#installation-on-archlinux)
- [Installation from source](#installation-from-source)
- [Common pre-requirements](#common-pre-requirements)
- [Linux-specific pre-requirements](#linux-specific-pre-requirements)
- [Windows-specific pre-requirements (optional)](#windows-specific-pre-requirements-optional)
- [Download the source code](#download-the-source-code)
- [Building](#building)
- [Install via cabal](#install-via-cabal)
- [Install specific GHC Version](#install-specific-ghc-version)
- [Multiple versions of HIE (optional)](#multiple-versions-of-hie-optional)
- [Configuration](#configuration)
- [Explicit Configuration](#explicit-configuration)
- [Editor Integration](#editor-integration)
- [Using HIE with VS Code](#using-hie-with-vs-code)
- [Using VS Code with Nix](#using-vs-code-with-nix)
- [Using HIE with Sublime Text](#using-hie-with-sublime-text)
- [Using HIE with Vim or Neovim](#using-hie-with-vim-or-neovim)
- [Coc](#coc)
- [LanguageClient-neovim](#languageclient-neovim)
- [vim-plug](#vim-plug)
- [Clone the LanguageClient-neovim repo](#clone-the-languageclient-neovim-repo)
- [Sample `~/.vimrc`](#sample-vimrc)
- [Using HIE with Atom](#using-hie-with-atom)
- [Using HIE with Emacs](#using-hie-with-emacs)
- [Using HIE with Spacemacs](#using-hie-with-spacemacs)
- [Using HIE with Spacemacs on Nix Based Projects](#using-hie-with-spacemacs-on-nix-based-projects)
- [Using HIE with Oni](#using-hie-with-oni)
- [Docs on hover/completion](#docs-on-hovercompletion)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [Planned Features](#planned-features)
- [It's time to join the project!](#its-time-to-join-the-project)
- [Documentation](#documentation)
- [Architecture](#architecture)
- [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting)
- [Emacs](#emacs)
- [Parse errors, file state going out of sync](#parse-errors-file-state-going-out-of-sync)
- [`emacs-direnv` loads environment too late](#emacs-direnv-loads-environment-too-late)
- [DYLD on macOS](#dyld-on-macos)
- [macOS: Got error while installing GHC 8.6.1 or 8.6.2 - dyld: Library not loaded: /usr/local/opt/gmp/lib/libgmp.10.dylib](#macos-got-error-while-installing-ghc-861-or-862---dyld-library-not-loaded-usrlocaloptgmpliblibgmp10dylib)
- [macOS: Got error while processing diagnostics: unable to load package `integer-gmp-1.0.2.0`](#macos-got-error-while-processing-diagnostics-unable-to-load-package-integer-gmp-1020)
- [cannot satisfy -package-id \](#cannot-satisfy--package-id-package)
- [Is \ base-x?](#is-package-base-x)
- [Is there a hash (#) after \?](#is-there-a-hash--after-package)
- [Otherwise](#otherwise)
- [Nix: cabal-helper, No such file or directory](#nix-cabal-helper-no-such-file-or-directory)
- [Liquid Haskell](#liquid-haskell)
## Features
- Supports plain GHC projects, cabal projects(sandboxed and non sandboxed) and stack projects
- Fast due to caching of compile info
- Uses LSP, so should be easy to integrate with a wide selection of editors
- Diagnostics via hlint and GHC warnings/errors

- Code actions and quick fixes via apply-refact

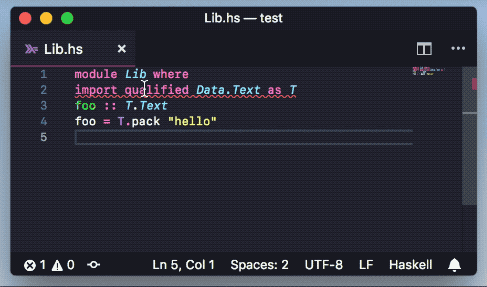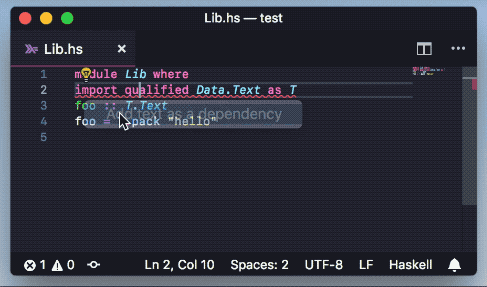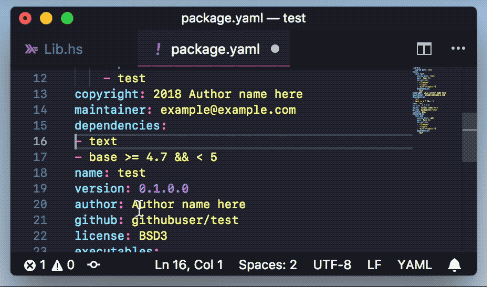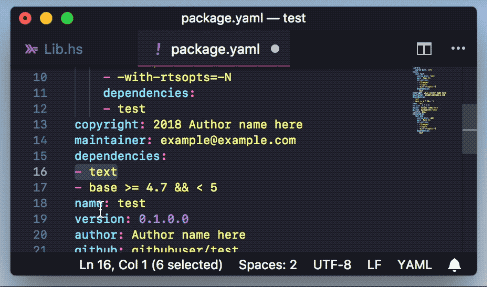
- Type information and documentation(via haddock) on hover

- Jump to definition
- List all top level definitions

- Highlight references in document

- Completion

- Formatting via brittany

- Renaming via HaRe

- Add packages to cabal and hpack package files
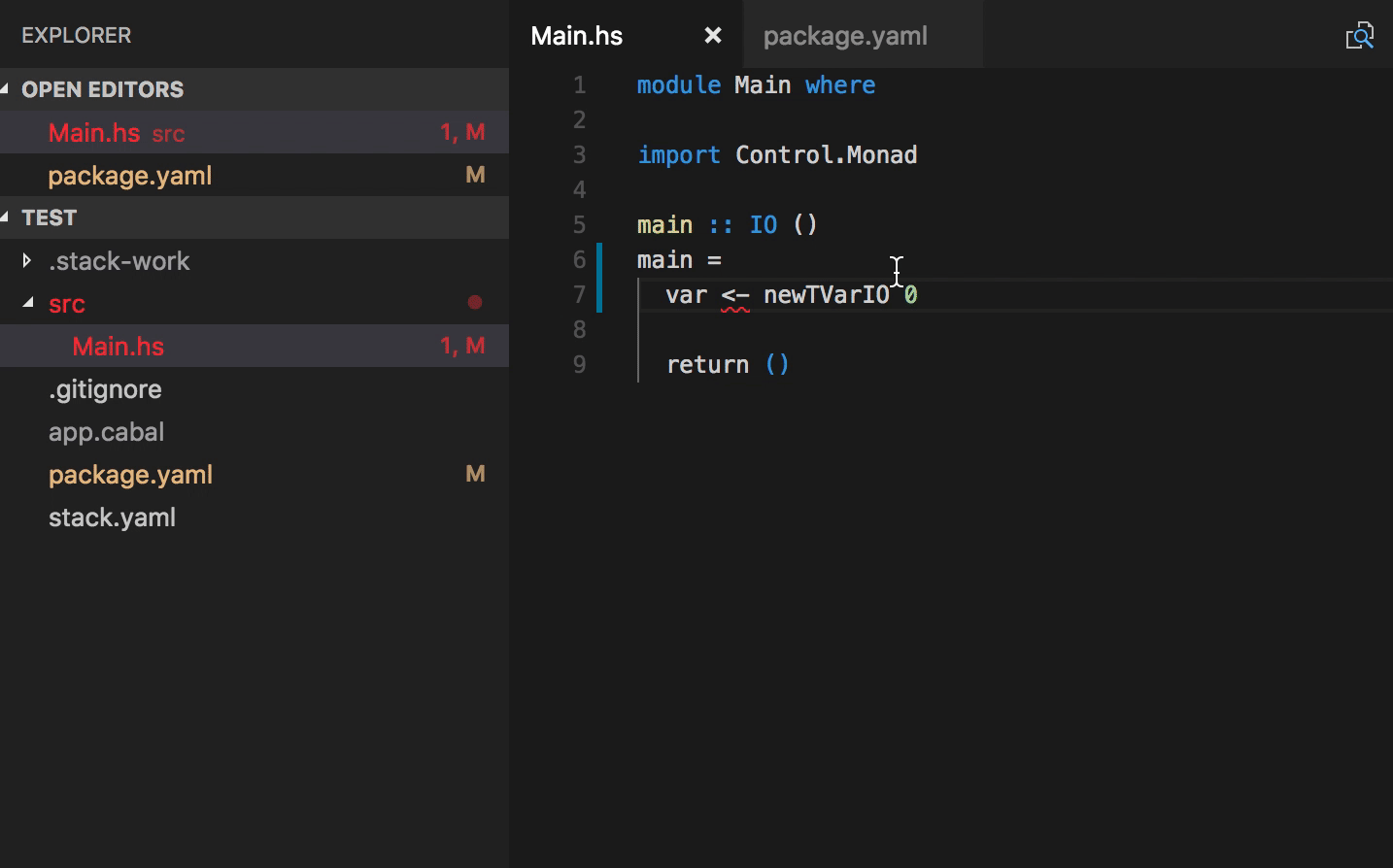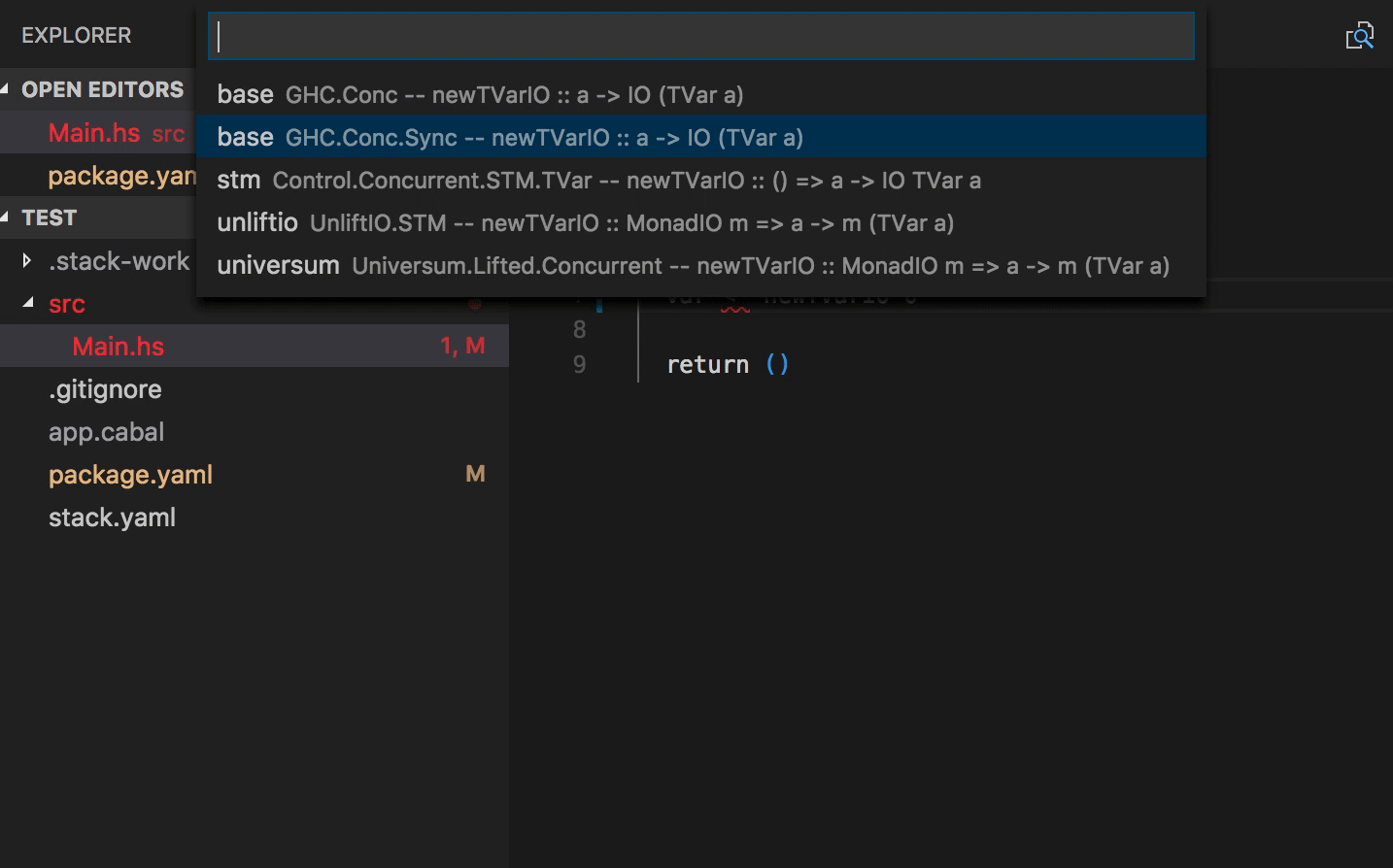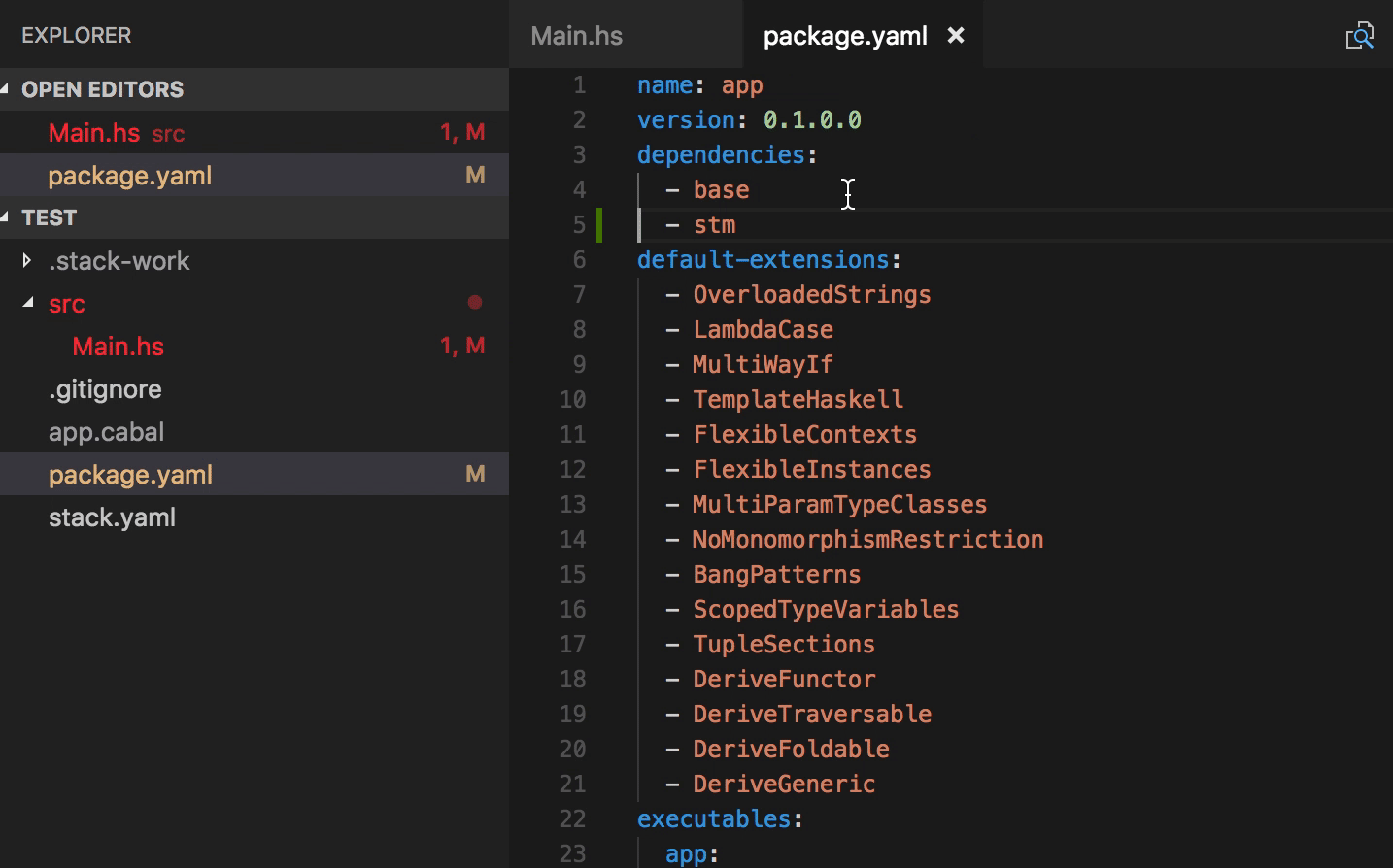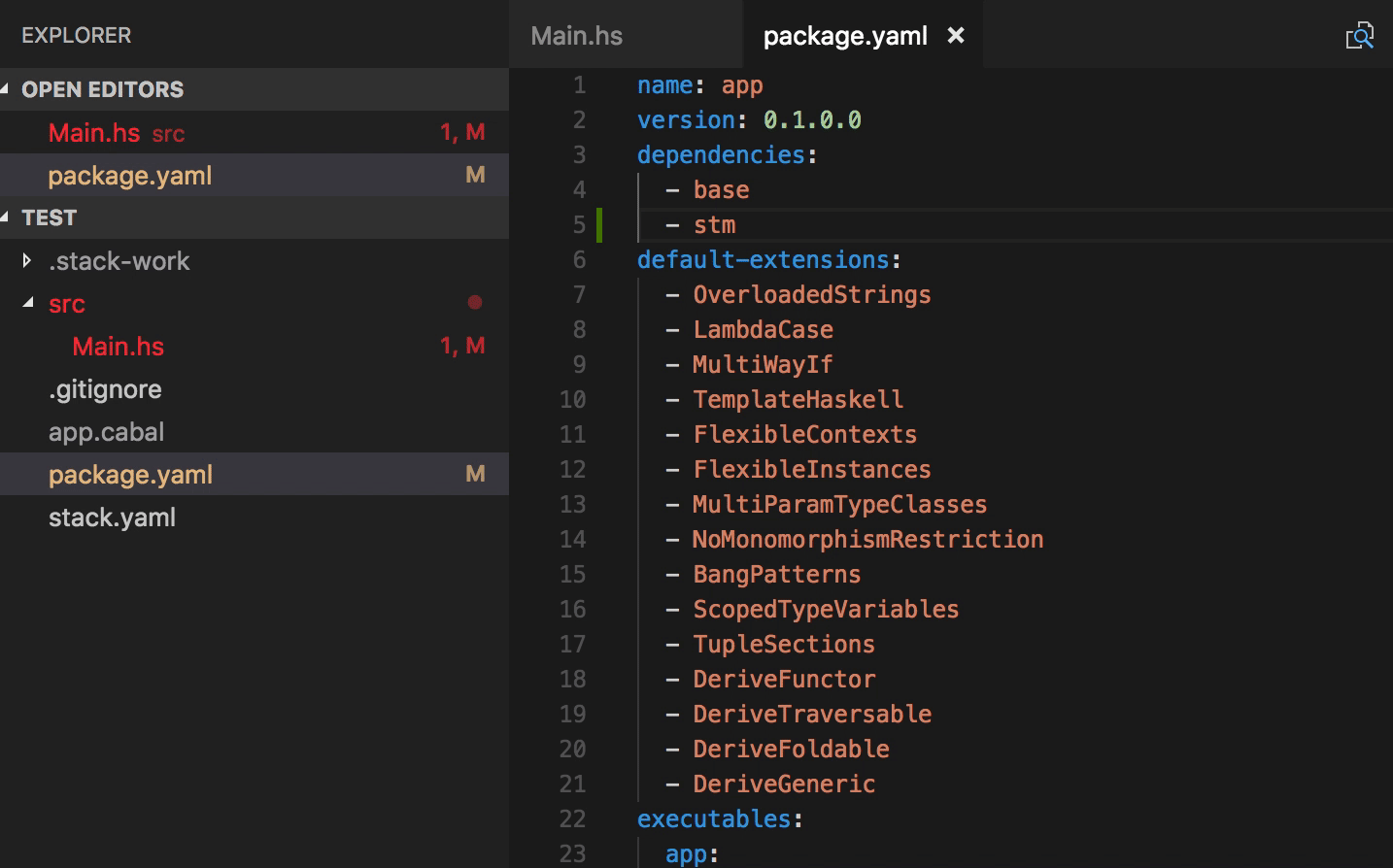
- Typo quick fixes
- Add missing imports (via hsimport)
## Installation
### Installation with Nix
Follow the instructions at https://github.com/Infinisil/all-hies
### Installation on ArchLinux
An [haskell-ide-engine](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/haskell-ide-engine/) package is available on the AUR.
Using [Aura](https://github.com/aurapm/aura):
```
# aura -A haskell-ide-engine
```
### Installation from source
To install HIE, you need stack version >= 1.7.1.
HIE builds from source code, so there's a couple of extra steps.
#### Common pre-requirements
* `stack` must be in your PATH
* `git` must be in your PATH
* Stack local bin directory must be in your PATH. Get it with `stack path --local-bin`
Tip: you can quickly check if some command is in your path by running the command.
If you receive some meaningful output instead of "command not found"-like message
then it means you have the command in PATH.
#### Linux-specific pre-requirements
On Linux you will need install a couple of extra libraries (for Unicode ([ICU](http://site.icu-project.org/)) and [NCURSES](https://www.gnu.org/software/ncurses/)):
**Debian/Ubuntu**:
```bash
sudo apt install libicu-dev libtinfo-dev libgmp-dev
```
**Fedora**:
```bash
sudo dnf install libicu-devel ncurses-devel
```
#### Windows-specific pre-requirements (optional)
In order to avoid problems with long paths on Windows you can do the following:
1. Edit the group policy: set "Enable Win32 long paths" to "Enabled" (Works
only for Windows 10).
2. Clone the `haskell-ide-engine` to the root of your logical drive (e.g. to
`C:\hie`)
#### Download the source code
```bash
git clone https://github.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine --recurse-submodules
cd haskell-ide-engine
```
#### Building
Uses the [shake](https://shakebuild.com/) build system for predictable builds.
Note, on first invocation of the build script, a GHC is being installed for execution.
The GHC used for the `install.hs` can be adjusted in `shake.yaml` by using a different resolver.
Available commands can be seen with:
```bash
stack ./install.hs help
```
Remember, this will take time to download a Stackage-LTS and an appropriate GHC. However, afterwards all commands should work as expected.
##### Install via cabal
The install-script can be invoked via `cabal` instead of `stack` with the command
```bash
cabal v2-run ./install.hs --project-file install/shake.project
```
Running the script with cabal on windows requires a cabal version greater or equal to `3.0.0.0`.
Unfortunately, it is still required to have `stack` installed so that the install-script can locate the `local-bin` directory (on Linux `~/.local/bin`) and copy the `hie` binaries to `hie-x.y.z`, which is required for the `hie-wrapper` to function as expected.
For brevity, only the `stack`-based commands are presented in the following sections.
##### Install cabal using stack
Although you can use hie for stack based projects (those which have a `stack.yaml` in the project base directory) without having cabal installed, you will need it for cabal based projects (with only a `.cabal` file or a `cabal.project` one in the project base directory).
You can install an appropiate cabal version using stack by running:
```bash
stack ./install.hs stack-install-cabal
```
##### Install specific GHC Version
Install **Nightly** (and hoogle docs):
```bash
stack ./install.hs hie-8.6.4
stack ./install.hs build-data
```
Install **LTS** (and hoogle docs):
```bash
stack ./install.hs hie-8.4.4
stack ./install.hs build-data
```
The Haskell IDE Engine can also be built with `cabal new-build` instead of `stack build`.
This has the advantage that you can decide how the GHC versions have been installed.
However, this approach does currently not work for windows due to a missing feature upstream.
To see what GHC versions are available, the command `stack install.hs cabal-ghcs` can be used.
It will list all GHC versions that are on the path and their respective installation directory.
If you think, this list is incomplete, you can try to modify the PATH variable, such that the executables can be found.
Note, that the targets `cabal-build`, `cabal-build-data` and `cabal-build-all` depend on the found GHC versions.
They install Haskell IDE Engine only for the found GHC versions.
An example output is:
```bash
> stack install.hs cabal-ghcs
******************************************************************
Found the following GHC paths:
ghc-8.4.4: /opt/bin/ghc-8.4.4
ghc-8.6.2: /opt/bin/ghc-8.6.2
******************************************************************
```
If your desired ghc has been found, you use it to install Haskell IDE Engine.
```bash
stack install.hs cabal-hie-8.4.4
stack install.hs cabal-build-data
```
To install HIE for all GHC versions that are present on your system, use:
```bash
stack ./install.hs cabal-build-all
```
In general, targets that use `cabal` instead of `stack` are prefixed with `cabal-*` and are identical to their counterpart, except they do not install a GHC if it is missing but fail.
##### Multiple versions of HIE (optional)
If you installed multiple versions of HIE then you will need to use a wrapper script.
Wrapper script will analyze your project, find suitable version of HIE and launch it.
Enable it by editing VS Code settings like that:
```json
"languageServerHaskell.useCustomHieWrapper": true,
"languageServerHaskell.useCustomHieWrapperPath": "hie-wrapper",
```
## Configuration
There are some settings that can be configured via a `settings.json` file:
```json
{
"languageServerHaskell": {
"hlintOn": Boolean,
"maxNumberOfProblems": Number
"diagnosticsDebounceDuration" : Number
"liquidOn" : Bool (default False)
"completionSnippetsOn" : Bool (default True)
"formatOnImportOn" : Bool (default True)
"formattingProvider" : String (default "brittany",
alternate "floskell")
}
}
```
- VS Code: These settings will show up in the settings window
- LanguageClient-neovim: Create this file in `$projectdir/.vim/settings.json` or set `g:LanguageClient_settingsPath`
## Explicit Configuration
**For a full explanation of possible configuration, we refer to [hie-bios/README](https://github.com/mpickering/hie-bios/blob/master/README.md).**
The user can place a `hie.yaml` file in the root of the workspace which
describes how to setup the environment. For example, to explicitly state
that you want to use `stack` then the configuration file would look like:
```yaml
cradle: {stack}
```
If you use `cabal` then you probably need to specify which component you want
to use.
```yaml
cradle:
cabal:
component: "lib:haskell-ide-engine"
```
Or you can explicitly state the program which should be used to collect
the options by supplying the path to the program. It is interpreted
relative to the current working directory if it is not an absolute path.
```yaml
cradle:
bios:
program: ".hie-bios"
```
The complete configuration is a subset of
```yaml
cradle:
cabal:
component: "optional component name"
stack:
bazel:
obelisk:
bios:
program: "program to run"
dependency-program: "optional program to run"
direct:
arguments: ["list","of","ghc","arguments"]
default:
none:
dependencies:
- someDep
```
There is also support for multiple cradles in a single `hie.yaml`. An example configuration for Haskell IDE Engine:
```yaml
cradle:
multi:
- path: ./test/dispatcher/
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "test:dispatcher-test"
- path: ./test/functional/
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "test:func-test"
- path: ./test/unit/
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "test:unit-test"
- path: ./hie-plugin-api/
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "lib:hie-plugin-api"
- path: ./app/MainHie.hs
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "exe:hie"
- path: ./app/HieWrapper.hs
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "exe:hie-wrapper"
- path: ./
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "lib:haskell-ide-engine"
```
## Editor Integration
Note to editor integrators: there is now a `hie-wrapper` executable, which is installed alongside the `hie` executable. When this is invoked in the project root directory, it attempts to work out the GHC version used in the project, and then launch the matching `hie` executable.
All of the editor integrations assume that you have already installed HIE (see above) and that `stack` put the `hie` binary in your path (usually `~/.local/bin` on linux and macOS).
### Using HIE with VS Code
Install from
[the VSCode marketplace](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=alanz.vscode-hie-server), or manually from the repository [vscode-hie-server](https://github.com/alanz/vscode-hie-server).
#### Using VS Code with Nix
`.config/nixpkgs/config.nix` sample:
``` nix
with import {};
let
hie = (import (fetchFromGitHub {
owner="domenkozar";
repo="hie-nix";
rev="e3113da";
sha256="05rkzjvzywsg66iafm84xgjlkf27yfbagrdcb8sc9fd59hrzyiqk";
}) {}).hie84;
in
{
allowUnfree = true;
packageOverrides = pkgs: rec {
vscode = pkgs.vscode.overrideDerivation (old: {
postFixup = ''
wrapProgram $out/bin/code --prefix PATH : ${lib.makeBinPath [hie]}
'';
});
};
}
```
### Using HIE with Sublime Text
* Make sure HIE is installed (see above) and that the directory stack put the `hie` binary in is in your path
* (usually `~/.local/bin` on unix)
* Install [LSP](https://packagecontrol.io/packages/LSP) using [Package Control](https://packagecontrol.io/)
* From Sublime Text, press Command+Shift+P and search for Preferences: LSP Settings
* Paste in these settings. Make sure to change the command path to your `hie`
```
{
"clients": {
"haskell-ide-engine": {
"command": ["hie"],
"scopes": ["source.haskell"],
"syntaxes": ["Packages/Haskell/Haskell.sublime-syntax"],
"languageId": "haskell",
},
},
}
```
Now open a Haskell project with Sublime Text. You should have these features available to you:
1. Errors are underlined in red
2. LSP: Show Diagnostics will show a list of hints and errors
3. LSP: Format Document will prettify the file
### Using HIE with Vim or Neovim
As above, make sure HIE is installed.
Then you can use [Coc](https://github.com/neoclide/coc.nvim), [LanguageClient-neovim](https://github.com/autozimu/LanguageClient-neovim)
or any other vim Langauge server protocol client.
Coc is recommend since it is the only complete LSP implementation for Vim and Neovim and offers snippets and floating documentation out of the box.
#### Coc
Follow Coc's [installation instructions](https://github.com/neoclide/coc.nvim),
Then issue `:CocConfig` and add the following to your Coc config file.
```jsonc
"languageserver": {
"haskell": {
"command": "hie-wrapper",
"rootPatterns": [
".stack.yaml",
"cabal.config",
"package.yaml"
],
"filetypes": [
"hs",
"lhs",
"haskell"
],
"initializationOptions": {
"languageServerHaskell": {
}
},
}
}
```
#### LanguageClient-neovim
##### vim-plug
If you use [vim-plug](https://github.com/junegunn/vim-plug), then you can do this by e.g.,
including the following line in the Plug section of your `init.vim` or `~/.vimrc`:
```
Plug 'autozimu/LanguageClient-neovim', {
\ 'branch': 'next',
\ 'do': './install.sh'
\ }
```
and issuing a `:PlugInstall` command within Neovim or Vim.
##### Clone the LanguageClient-neovim repo
As an alternative to using [vim-plug](https://github.com/junegunn/vim-plug) shown above, clone [LanguageClient-neovim](https://github.com/autozimu/LanguageClient-neovim)
into `~/.vim/pack/XXX/start/`, where `XXX` is just a name for your "plugin suite".
##### Sample `~/.vimrc`
```vim
set rtp+=~/.vim/pack/XXX/start/LanguageClient-neovim
let g:LanguageClient_serverCommands = { 'haskell': ['hie-wrapper'] }
```
You'll probably want to add some mappings for common commands:
```vim
nnoremap :call LanguageClient_contextMenu()
map lk :call LanguageClient#textDocument_hover()
map lg :call LanguageClient#textDocument_definition()
map lr :call LanguageClient#textDocument_rename()
map lf :call LanguageClient#textDocument_formatting()
map lb :call LanguageClient#textDocument_references()
map la :call LanguageClient#textDocument_codeAction()
map ls :call LanguageClient#textDocument_documentSymbol()
```
Use Ctrl+xCtrl+o (``) to open up the auto-complete menu,
or for asynchronous auto-completion, follow the setup instructions on
[LanguageClient](https://github.com/autozimu/LanguageClient-neovim).
If you'd like diagnostics to be highlighted, add a highlight group for `ALEError`/`ALEWarning`/`ALEInfo`,
or customize ` g:LanguageClient_diagnosticsDisplay`:
```vim
hi link ALEError Error
hi Warning term=underline cterm=underline ctermfg=Yellow gui=undercurl guisp=Gold
hi link ALEWarning Warning
hi link ALEInfo SpellCap
```
If you're finding that the server isn't starting at the correct project root,
it may also be helpful to also specify root markers:
```vim
let g:LanguageClient_rootMarkers = ['*.cabal', 'stack.yaml']
```
### Using HIE with Atom
Make sure HIE is installed, then install the two Atom packages [atom-ide-ui](https://atom.io/packages/atom-ide-ui) and [ide-haskell-hie](https://atom.io/packages/ide-haskell-hie),
```bash
$ apm install language-haskell atom-ide-ui ide-haskell-hie
```
### Using HIE with Emacs
Install HIE along with the following emacs packages:
[lsp-mode](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-mode)
[lsp-ui](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-ui)
[lsp-haskell](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-haskell)
Make sure to follow the instructions in the README of each of these packages.
### Using HIE with Spacemacs
Install HIE, and then add the following to your `.spacemacs` config,
```lisp
(defun dotspacemacs/layers ()
"..."
(setq-default
;; ...
dotspacemacs-configuration-layers
'(
lsp
(haskell :variables ;; Or optionally just haskell without the variables.
haskell-completion-backend 'ghci
haskell-process-type 'stack-ghci)
)
dotspacemacs-additional-packages '(
(lsp-haskell :location (recipe :fetcher github :repo "emacs-lsp/lsp-haskell"))
)
;; ...
))
```
and then activate [`lsp-haskell`](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-haskell) in your `user-config` section,
```lisp
(defun dotspacemacs/user-config ()
"..."
(setq lsp-haskell-process-path-hie "hie-wrapper")
(require 'lsp-haskell)
(add-hook 'haskell-mode-hook #'lsp)
)
```
Now you should be able to use HIE in Spacemacs. I still recommend checking out [lsp-ui](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-ui) and [lsp-mode](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-mode).
### Using HIE with Spacemacs on Nix Based Projects
If you use HIE with spacemacs on nix-built haskell projects, you may want to try
out [this spacemacs layer](https://github.com/benkolera/spacemacs-hie-nix). It
has installation instructions which includes a nix expression to install
everything that hie needs in your environment. It wraps the hie binary calls to
use nix-sandbox to find the closest ancestor directory that has nixfiles.
It is still pretty new and may change drastically as the author understands the
lsp, lsp-ui, lsp-haskell, hie stack a bit better. PRs and feedback are very
welcome on the layer's repo if you find it useful and/or lacking in some way.
### Using HIE with Oni
[Oni](https://www.onivim.io/) (a Neovim GUI) added built-in support for HIE, using stack, in [#1918](https://github.com/onivim/oni/pull/1918/files). If you need to change the configuration for HIE, you can overwrite the following settings in your `~/.config/oni/config.tsx` file (accessible via the command palette and `Configuration: Edit User Config`),
```js
export const configuration = {
"language.haskell.languageServer.command": "stack",
"language.haskell.languageServer.arguments": ["exec", "--", "hie"],
"language.haskell.languageServer.rootFiles": [".git"],
"language.haskell.languageServer.configuration": {},
}
```
## Docs on hover/completion
HIE supports fetching docs from haddock on hover. It will fallback on using a hoogle db(generally located in ~/.hoogle on linux)
if no haddock documentation is found.
To generate haddock documentation for stack projects:
```bash
$ cd your-project-directory
$ stack haddock --keep-going
```
To enable documentation generation for cabal projects, add the following to your ~/.cabal/config
```
documentation: True
```
To generate a hoogle database that hie can use
```bash
$ cd haskell-ide-engine
$ stack --stack-yaml= exec hoogle generate
```
Or you can set the environment variable `HIE_HOOGLE_DATABASE` to specify a specific database.
## Contributing
### Planned Features
- [x] Multiproject support
- [ ] Project wide references
- [ ] Cross project find definition
- [ ] New-build support
- [ ] HaRe refactorings
- [ ] More code actions
- [ ] Cross project/dependency Find Definition
- [ ] Case splitting, type insertion etc.
This project is not started from scratch:
1. See why [we should supersede previous tools](/docs/Challenges.md)
2. Check the [list of existing tools and functionality](/docs/Tools.md)
3. See more [other tools and IDEs for inspiration](/docs/Inspirations.md)
### It's time to join the project!
:heart: Haskell tooling dream is near, we need your help! :heart:
- Register in [our google group mailing list](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/haskell-ide).
- Join [our IRC channel](https://webchat.freenode.net/?channels=haskell-ide-engine) at `#haskell-ide-engine` on `freenode`.
- Fork this repo and hack as much as you can.
- Ask @alanz or @hvr to join the project.
## Documentation
All the documentation is in [the docs folder](/docs) at the root of this project.
### Architecture
Have a look at
- the [Architecture discussion](docs/Architecture.md),
- [Protocol discussion](docs/Protocol.md) and
- [Design discussion](docs/Design.md).
## Troubleshooting
### Emacs
#### Parse errors, file state going out of sync
With the `lsp-mode` client for Emacs, it seems that the document can very easily get out of sync between, which leads to parse errors being displayed. To fix this, enable full document synchronization with
```elisp
(setq lsp-document-sync-method 'full)
```
#### [`emacs-direnv`](https://github.com/wbolster/emacs-direnv) loads environment too late
`emacs-direnv` sometimes loads the environment too late, meaning `lsp-mode` won't be able to find correct GHC/cabal versions. To fix this, add a direnv update hook *after* adding the lsp hook for `haskell-mode` (meaning the direnv hook is executed first, because hooks are LIFO):
```elisp
(add-hook 'haskell-mode-hook 'lsp)
(add-hook 'haskell-mode-hook 'direnv-update-environment)
```
### DYLD on macOS
If you hit a problem that looks like ```can't load .so/.DLL for: libiconv.dylib (dlopen(libiconv.dylib, 5): image not found)```, it means that libraries cannot be found in the library path. We can hint where to look for them and append more paths to `DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH`.
```
export DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH="$DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/lib:/usr/local/lib"
```
On practice `/usr/local/lib` is full of dylibs linked by `brew`. After you amend `DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH`, some of the previously compiled application might not work and yell about incorrect linking, for example, `dyld: Symbol not found: __cg_jpeg_resync_to_restart`. You may need to look up where it comes from and remove clashing links, in this case it were clashing images libs:
```sh
$ brew unlink libjpeg
$ brew unlink libtiff
$ brew unlink libpng
```
Recompile.
### macOS: Got error while installing GHC 8.6.1 or 8.6.2 - dyld: Library not loaded: /usr/local/opt/gmp/lib/libgmp.10.dylib
These builds have a dependency on [homebrew](https://brew.sh)'s `gmp` library. Install with brew: `brew install gmp`.
[Should be fixed in GHC 8.6.3.](https://ghc.haskell.org/trac/ghc/ticket/15769)
### macOS: Got error while processing diagnostics: unable to load package `integer-gmp-1.0.2.0`
[Rename the file](https://github.com/alanz/vscode-hie-server/issues/89#issuecomment-398212122) at `~/.stack/programs/x86_64-osx/ghc-8.4.3/lib/ghc-8.4.3/integer-gmp-1.0.2.0/HSinteger-gmp-1.0.2.0.o` to a temporary name.
[Should be fixed in GHC 8.8.1.](https://ghc.haskell.org/trac/ghc/ticket/15105)
### cannot satisfy -package-id \
#### Is \ base-x?
Make sure that the GHC version of HIE matches the one of the project. After that run
```
$ cabal configure
```
and then restart HIE (e.g. by restarting your editor).
#### Is there a hash (#) after \?
Delete any `.ghc.environment*` files in your project root and try again. (At the time of writing, cabal new-style projects are not supported with ghc-mod)
#### Otherwise
Try running `cabal update`.
### Nix: cabal-helper, No such file or directory
An error on stderr like
```
cabal-helper-wrapper: /home/<...>/.cache/cabal-helper/cabal-helper<...>: createProcess: runInteractiveProcess:
exec: does not exist (No such file or directory)
```
can happen because cabal-helper compiles and runs above executable at runtime without using nix-build, which means a Nix garbage collection can delete the paths it depends on. Delete ~/.cache/cabal-helper and restart HIE to fix this.
### Liquid Haskell
Liquid Haskell requires an SMT solver on the path. We do not take care of installing one, thus, Liquid Haskell will not run until one is installed.
The recommended SMT solver is [z3](https://github.com/Z3Prover/z3). To run the tests, it is also required to have an SMT solver on the path, otherwise the tests will fail for Liquid Haskell.
### Profiling `haskell-ide-engine`.
If you think `haskell-ide-engine` is using a lot of memory then the most useful
thing you can do is prepare a profile of the memory usage whilst you're using
the program.
1. Add `profiling: True` to the cabal.project file of `haskell-ide-engine
2. `cabal new-build hie`
3. (IMPORTANT) Add `profiling: True` to the `cabal.project` file of the project you want to profile.
4. Make a wrapper script which calls the `hie` you built in step 2 with the additional options `+RTS -hd -l-au`
5. Modify your editor settings to call this wrapper script instead of looking for `hie` on the path
6. Try using `h-i-e` as normal and then process the `*.eventlog` which will be created using `eventlog2html`.
7. Repeat the process again using different profiling options if you like.
[![License BSD3][badge-license]][license]
[![CircleCI][badge-circleci]][circleci]
[![AppVeyor][badge-appveyor]][appveyor]
[](https://www.codetriage.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine)
[badge-license]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-BSD3-green.svg?dummy
[license]: https://github.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/blob/master/LICENSE
[badge-circleci]: https://img.shields.io/circleci/project/github/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/master.svg
[circleci]: https://circleci.com/gh/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/
[badge-appveyor]: https://ci.appveyor.com/api/projects/status/6hit7mxvgdrao3q0?svg=true
[appveyor]: https://ci.appveyor.com/project/Bubba/haskell-ide-engine-74xec
This project aims to be __the universal interface__ to __a growing number of Haskell tools__, providing a __full-featured and easy to query backend__ for editors and IDEs that require Haskell-specific functionality.
__We are currently focusing on using the [Language Server Protocol](https://github.com/Microsoft/language-server-protocol/blob/master/protocol.md) as the interface via which
we talk to clients.__
- [Haskell IDE Engine (HIE)](#haskell-ide-engine-hie)
- [Features](#features)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Installation with Nix](#installation-with-nix)
- [Installation on ArchLinux](#installation-on-archlinux)
- [Installation from source](#installation-from-source)
- [Common pre-requirements](#common-pre-requirements)
- [Linux-specific pre-requirements](#linux-specific-pre-requirements)
- [Windows-specific pre-requirements (optional)](#windows-specific-pre-requirements-optional)
- [Download the source code](#download-the-source-code)
- [Building](#building)
- [Install via cabal](#install-via-cabal)
- [Install specific GHC Version](#install-specific-ghc-version)
- [Multiple versions of HIE (optional)](#multiple-versions-of-hie-optional)
- [Configuration](#configuration)
- [Explicit Configuration](#explicit-configuration)
- [Editor Integration](#editor-integration)
- [Using HIE with VS Code](#using-hie-with-vs-code)
- [Using VS Code with Nix](#using-vs-code-with-nix)
- [Using HIE with Sublime Text](#using-hie-with-sublime-text)
- [Using HIE with Vim or Neovim](#using-hie-with-vim-or-neovim)
- [Coc](#coc)
- [LanguageClient-neovim](#languageclient-neovim)
- [vim-plug](#vim-plug)
- [Clone the LanguageClient-neovim repo](#clone-the-languageclient-neovim-repo)
- [Sample `~/.vimrc`](#sample-vimrc)
- [Using HIE with Atom](#using-hie-with-atom)
- [Using HIE with Emacs](#using-hie-with-emacs)
- [Using HIE with Spacemacs](#using-hie-with-spacemacs)
- [Using HIE with Spacemacs on Nix Based Projects](#using-hie-with-spacemacs-on-nix-based-projects)
- [Using HIE with Oni](#using-hie-with-oni)
- [Docs on hover/completion](#docs-on-hovercompletion)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [Planned Features](#planned-features)
- [It's time to join the project!](#its-time-to-join-the-project)
- [Documentation](#documentation)
- [Architecture](#architecture)
- [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting)
- [Emacs](#emacs)
- [Parse errors, file state going out of sync](#parse-errors-file-state-going-out-of-sync)
- [`emacs-direnv` loads environment too late](#emacs-direnv-loads-environment-too-late)
- [DYLD on macOS](#dyld-on-macos)
- [macOS: Got error while installing GHC 8.6.1 or 8.6.2 - dyld: Library not loaded: /usr/local/opt/gmp/lib/libgmp.10.dylib](#macos-got-error-while-installing-ghc-861-or-862---dyld-library-not-loaded-usrlocaloptgmpliblibgmp10dylib)
- [macOS: Got error while processing diagnostics: unable to load package `integer-gmp-1.0.2.0`](#macos-got-error-while-processing-diagnostics-unable-to-load-package-integer-gmp-1020)
- [cannot satisfy -package-id \](#cannot-satisfy--package-id-package)
- [Is \ base-x?](#is-package-base-x)
- [Is there a hash (#) after \?](#is-there-a-hash--after-package)
- [Otherwise](#otherwise)
- [Nix: cabal-helper, No such file or directory](#nix-cabal-helper-no-such-file-or-directory)
- [Liquid Haskell](#liquid-haskell)
## Features
- Supports plain GHC projects, cabal projects(sandboxed and non sandboxed) and stack projects
- Fast due to caching of compile info
- Uses LSP, so should be easy to integrate with a wide selection of editors
- Diagnostics via hlint and GHC warnings/errors

- Code actions and quick fixes via apply-refact

- Type information and documentation(via haddock) on hover

- Jump to definition

- List all top level definitions

- Highlight references in document

- Completion

- Formatting via brittany

- Renaming via HaRe

- Add packages to cabal and hpack package files


- Typo quick fixes

- Add missing imports (via hsimport)

## Installation
### Installation with Nix
Follow the instructions at https://github.com/Infinisil/all-hies
### Installation on ArchLinux
An [haskell-ide-engine](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/haskell-ide-engine/) package is available on the AUR.
Using [Aura](https://github.com/aurapm/aura):
```
# aura -A haskell-ide-engine
```
### Installation from source
To install HIE, you need stack version >= 1.7.1.
HIE builds from source code, so there's a couple of extra steps.
#### Common pre-requirements
* `stack` must be in your PATH
* `git` must be in your PATH
* Stack local bin directory must be in your PATH. Get it with `stack path --local-bin`
Tip: you can quickly check if some command is in your path by running the command.
If you receive some meaningful output instead of "command not found"-like message
then it means you have the command in PATH.
#### Linux-specific pre-requirements
On Linux you will need install a couple of extra libraries (for Unicode ([ICU](http://site.icu-project.org/)) and [NCURSES](https://www.gnu.org/software/ncurses/)):
**Debian/Ubuntu**:
```bash
sudo apt install libicu-dev libtinfo-dev libgmp-dev
```
**Fedora**:
```bash
sudo dnf install libicu-devel ncurses-devel
```
#### Windows-specific pre-requirements (optional)
In order to avoid problems with long paths on Windows you can do the following:
1. Edit the group policy: set "Enable Win32 long paths" to "Enabled" (Works
only for Windows 10).
2. Clone the `haskell-ide-engine` to the root of your logical drive (e.g. to
`C:\hie`)
#### Download the source code
```bash
git clone https://github.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine --recurse-submodules
cd haskell-ide-engine
```
#### Building
Uses the [shake](https://shakebuild.com/) build system for predictable builds.
Note, on first invocation of the build script, a GHC is being installed for execution.
The GHC used for the `install.hs` can be adjusted in `shake.yaml` by using a different resolver.
Available commands can be seen with:
```bash
stack ./install.hs help
```
Remember, this will take time to download a Stackage-LTS and an appropriate GHC. However, afterwards all commands should work as expected.
##### Install via cabal
The install-script can be invoked via `cabal` instead of `stack` with the command
```bash
cabal v2-run ./install.hs --project-file install/shake.project
```
Running the script with cabal on windows requires a cabal version greater or equal to `3.0.0.0`.
Unfortunately, it is still required to have `stack` installed so that the install-script can locate the `local-bin` directory (on Linux `~/.local/bin`) and copy the `hie` binaries to `hie-x.y.z`, which is required for the `hie-wrapper` to function as expected.
For brevity, only the `stack`-based commands are presented in the following sections.
##### Install cabal using stack
Although you can use hie for stack based projects (those which have a `stack.yaml` in the project base directory) without having cabal installed, you will need it for cabal based projects (with only a `.cabal` file or a `cabal.project` one in the project base directory).
You can install an appropiate cabal version using stack by running:
```bash
stack ./install.hs stack-install-cabal
```
##### Install specific GHC Version
Install **Nightly** (and hoogle docs):
```bash
stack ./install.hs hie-8.6.4
stack ./install.hs build-data
```
Install **LTS** (and hoogle docs):
```bash
stack ./install.hs hie-8.4.4
stack ./install.hs build-data
```
The Haskell IDE Engine can also be built with `cabal new-build` instead of `stack build`.
This has the advantage that you can decide how the GHC versions have been installed.
However, this approach does currently not work for windows due to a missing feature upstream.
To see what GHC versions are available, the command `stack install.hs cabal-ghcs` can be used.
It will list all GHC versions that are on the path and their respective installation directory.
If you think, this list is incomplete, you can try to modify the PATH variable, such that the executables can be found.
Note, that the targets `cabal-build`, `cabal-build-data` and `cabal-build-all` depend on the found GHC versions.
They install Haskell IDE Engine only for the found GHC versions.
An example output is:
```bash
> stack install.hs cabal-ghcs
******************************************************************
Found the following GHC paths:
ghc-8.4.4: /opt/bin/ghc-8.4.4
ghc-8.6.2: /opt/bin/ghc-8.6.2
******************************************************************
```
If your desired ghc has been found, you use it to install Haskell IDE Engine.
```bash
stack install.hs cabal-hie-8.4.4
stack install.hs cabal-build-data
```
To install HIE for all GHC versions that are present on your system, use:
```bash
stack ./install.hs cabal-build-all
```
In general, targets that use `cabal` instead of `stack` are prefixed with `cabal-*` and are identical to their counterpart, except they do not install a GHC if it is missing but fail.
##### Multiple versions of HIE (optional)
If you installed multiple versions of HIE then you will need to use a wrapper script.
Wrapper script will analyze your project, find suitable version of HIE and launch it.
Enable it by editing VS Code settings like that:
```json
"languageServerHaskell.useCustomHieWrapper": true,
"languageServerHaskell.useCustomHieWrapperPath": "hie-wrapper",
```
## Configuration
There are some settings that can be configured via a `settings.json` file:
```json
{
"languageServerHaskell": {
"hlintOn": Boolean,
"maxNumberOfProblems": Number
"diagnosticsDebounceDuration" : Number
"liquidOn" : Bool (default False)
"completionSnippetsOn" : Bool (default True)
"formatOnImportOn" : Bool (default True)
"formattingProvider" : String (default "brittany",
alternate "floskell")
}
}
```
- VS Code: These settings will show up in the settings window
- LanguageClient-neovim: Create this file in `$projectdir/.vim/settings.json` or set `g:LanguageClient_settingsPath`
## Explicit Configuration
**For a full explanation of possible configuration, we refer to [hie-bios/README](https://github.com/mpickering/hie-bios/blob/master/README.md).**
The user can place a `hie.yaml` file in the root of the workspace which
describes how to setup the environment. For example, to explicitly state
that you want to use `stack` then the configuration file would look like:
```yaml
cradle: {stack}
```
If you use `cabal` then you probably need to specify which component you want
to use.
```yaml
cradle:
cabal:
component: "lib:haskell-ide-engine"
```
Or you can explicitly state the program which should be used to collect
the options by supplying the path to the program. It is interpreted
relative to the current working directory if it is not an absolute path.
```yaml
cradle:
bios:
program: ".hie-bios"
```
The complete configuration is a subset of
```yaml
cradle:
cabal:
component: "optional component name"
stack:
bazel:
obelisk:
bios:
program: "program to run"
dependency-program: "optional program to run"
direct:
arguments: ["list","of","ghc","arguments"]
default:
none:
dependencies:
- someDep
```
There is also support for multiple cradles in a single `hie.yaml`. An example configuration for Haskell IDE Engine:
```yaml
cradle:
multi:
- path: ./test/dispatcher/
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "test:dispatcher-test"
- path: ./test/functional/
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "test:func-test"
- path: ./test/unit/
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "test:unit-test"
- path: ./hie-plugin-api/
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "lib:hie-plugin-api"
- path: ./app/MainHie.hs
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "exe:hie"
- path: ./app/HieWrapper.hs
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "exe:hie-wrapper"
- path: ./
config:
cradle:
cabal:
component: "lib:haskell-ide-engine"
```
## Editor Integration
Note to editor integrators: there is now a `hie-wrapper` executable, which is installed alongside the `hie` executable. When this is invoked in the project root directory, it attempts to work out the GHC version used in the project, and then launch the matching `hie` executable.
All of the editor integrations assume that you have already installed HIE (see above) and that `stack` put the `hie` binary in your path (usually `~/.local/bin` on linux and macOS).
### Using HIE with VS Code
Install from
[the VSCode marketplace](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=alanz.vscode-hie-server), or manually from the repository [vscode-hie-server](https://github.com/alanz/vscode-hie-server).
#### Using VS Code with Nix
`.config/nixpkgs/config.nix` sample:
``` nix
with import {};
let
hie = (import (fetchFromGitHub {
owner="domenkozar";
repo="hie-nix";
rev="e3113da";
sha256="05rkzjvzywsg66iafm84xgjlkf27yfbagrdcb8sc9fd59hrzyiqk";
}) {}).hie84;
in
{
allowUnfree = true;
packageOverrides = pkgs: rec {
vscode = pkgs.vscode.overrideDerivation (old: {
postFixup = ''
wrapProgram $out/bin/code --prefix PATH : ${lib.makeBinPath [hie]}
'';
});
};
}
```
### Using HIE with Sublime Text
* Make sure HIE is installed (see above) and that the directory stack put the `hie` binary in is in your path
* (usually `~/.local/bin` on unix)
* Install [LSP](https://packagecontrol.io/packages/LSP) using [Package Control](https://packagecontrol.io/)
* From Sublime Text, press Command+Shift+P and search for Preferences: LSP Settings
* Paste in these settings. Make sure to change the command path to your `hie`
```
{
"clients": {
"haskell-ide-engine": {
"command": ["hie"],
"scopes": ["source.haskell"],
"syntaxes": ["Packages/Haskell/Haskell.sublime-syntax"],
"languageId": "haskell",
},
},
}
```
Now open a Haskell project with Sublime Text. You should have these features available to you:
1. Errors are underlined in red
2. LSP: Show Diagnostics will show a list of hints and errors
3. LSP: Format Document will prettify the file
### Using HIE with Vim or Neovim
As above, make sure HIE is installed.
Then you can use [Coc](https://github.com/neoclide/coc.nvim), [LanguageClient-neovim](https://github.com/autozimu/LanguageClient-neovim)
or any other vim Langauge server protocol client.
Coc is recommend since it is the only complete LSP implementation for Vim and Neovim and offers snippets and floating documentation out of the box.
#### Coc
Follow Coc's [installation instructions](https://github.com/neoclide/coc.nvim),
Then issue `:CocConfig` and add the following to your Coc config file.
```jsonc
"languageserver": {
"haskell": {
"command": "hie-wrapper",
"rootPatterns": [
".stack.yaml",
"cabal.config",
"package.yaml"
],
"filetypes": [
"hs",
"lhs",
"haskell"
],
"initializationOptions": {
"languageServerHaskell": {
}
},
}
}
```
#### LanguageClient-neovim
##### vim-plug
If you use [vim-plug](https://github.com/junegunn/vim-plug), then you can do this by e.g.,
including the following line in the Plug section of your `init.vim` or `~/.vimrc`:
```
Plug 'autozimu/LanguageClient-neovim', {
\ 'branch': 'next',
\ 'do': './install.sh'
\ }
```
and issuing a `:PlugInstall` command within Neovim or Vim.
##### Clone the LanguageClient-neovim repo
As an alternative to using [vim-plug](https://github.com/junegunn/vim-plug) shown above, clone [LanguageClient-neovim](https://github.com/autozimu/LanguageClient-neovim)
into `~/.vim/pack/XXX/start/`, where `XXX` is just a name for your "plugin suite".
##### Sample `~/.vimrc`
```vim
set rtp+=~/.vim/pack/XXX/start/LanguageClient-neovim
let g:LanguageClient_serverCommands = { 'haskell': ['hie-wrapper'] }
```
You'll probably want to add some mappings for common commands:
```vim
nnoremap :call LanguageClient_contextMenu()
map lk :call LanguageClient#textDocument_hover()
map lg :call LanguageClient#textDocument_definition()
map lr :call LanguageClient#textDocument_rename()
map lf :call LanguageClient#textDocument_formatting()
map lb :call LanguageClient#textDocument_references()
map la :call LanguageClient#textDocument_codeAction()
map ls :call LanguageClient#textDocument_documentSymbol()
```
Use Ctrl+xCtrl+o (``) to open up the auto-complete menu,
or for asynchronous auto-completion, follow the setup instructions on
[LanguageClient](https://github.com/autozimu/LanguageClient-neovim).
If you'd like diagnostics to be highlighted, add a highlight group for `ALEError`/`ALEWarning`/`ALEInfo`,
or customize ` g:LanguageClient_diagnosticsDisplay`:
```vim
hi link ALEError Error
hi Warning term=underline cterm=underline ctermfg=Yellow gui=undercurl guisp=Gold
hi link ALEWarning Warning
hi link ALEInfo SpellCap
```
If you're finding that the server isn't starting at the correct project root,
it may also be helpful to also specify root markers:
```vim
let g:LanguageClient_rootMarkers = ['*.cabal', 'stack.yaml']
```
### Using HIE with Atom
Make sure HIE is installed, then install the two Atom packages [atom-ide-ui](https://atom.io/packages/atom-ide-ui) and [ide-haskell-hie](https://atom.io/packages/ide-haskell-hie),
```bash
$ apm install language-haskell atom-ide-ui ide-haskell-hie
```
### Using HIE with Emacs
Install HIE along with the following emacs packages:
[lsp-mode](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-mode)
[lsp-ui](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-ui)
[lsp-haskell](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-haskell)
Make sure to follow the instructions in the README of each of these packages.
### Using HIE with Spacemacs
Install HIE, and then add the following to your `.spacemacs` config,
```lisp
(defun dotspacemacs/layers ()
"..."
(setq-default
;; ...
dotspacemacs-configuration-layers
'(
lsp
(haskell :variables ;; Or optionally just haskell without the variables.
haskell-completion-backend 'ghci
haskell-process-type 'stack-ghci)
)
dotspacemacs-additional-packages '(
(lsp-haskell :location (recipe :fetcher github :repo "emacs-lsp/lsp-haskell"))
)
;; ...
))
```
and then activate [`lsp-haskell`](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-haskell) in your `user-config` section,
```lisp
(defun dotspacemacs/user-config ()
"..."
(setq lsp-haskell-process-path-hie "hie-wrapper")
(require 'lsp-haskell)
(add-hook 'haskell-mode-hook #'lsp)
)
```
Now you should be able to use HIE in Spacemacs. I still recommend checking out [lsp-ui](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-ui) and [lsp-mode](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-mode).
### Using HIE with Spacemacs on Nix Based Projects
If you use HIE with spacemacs on nix-built haskell projects, you may want to try
out [this spacemacs layer](https://github.com/benkolera/spacemacs-hie-nix). It
has installation instructions which includes a nix expression to install
everything that hie needs in your environment. It wraps the hie binary calls to
use nix-sandbox to find the closest ancestor directory that has nixfiles.
It is still pretty new and may change drastically as the author understands the
lsp, lsp-ui, lsp-haskell, hie stack a bit better. PRs and feedback are very
welcome on the layer's repo if you find it useful and/or lacking in some way.
### Using HIE with Oni
[Oni](https://www.onivim.io/) (a Neovim GUI) added built-in support for HIE, using stack, in [#1918](https://github.com/onivim/oni/pull/1918/files). If you need to change the configuration for HIE, you can overwrite the following settings in your `~/.config/oni/config.tsx` file (accessible via the command palette and `Configuration: Edit User Config`),
```js
export const configuration = {
"language.haskell.languageServer.command": "stack",
"language.haskell.languageServer.arguments": ["exec", "--", "hie"],
"language.haskell.languageServer.rootFiles": [".git"],
"language.haskell.languageServer.configuration": {},
}
```
## Docs on hover/completion
HIE supports fetching docs from haddock on hover. It will fallback on using a hoogle db(generally located in ~/.hoogle on linux)
if no haddock documentation is found.
To generate haddock documentation for stack projects:
```bash
$ cd your-project-directory
$ stack haddock --keep-going
```
To enable documentation generation for cabal projects, add the following to your ~/.cabal/config
```
documentation: True
```
To generate a hoogle database that hie can use
```bash
$ cd haskell-ide-engine
$ stack --stack-yaml= exec hoogle generate
```
Or you can set the environment variable `HIE_HOOGLE_DATABASE` to specify a specific database.
## Contributing
### Planned Features
- [x] Multiproject support
- [ ] Project wide references
- [ ] Cross project find definition
- [ ] New-build support
- [ ] HaRe refactorings
- [ ] More code actions
- [ ] Cross project/dependency Find Definition
- [ ] Case splitting, type insertion etc.
This project is not started from scratch:
1. See why [we should supersede previous tools](/docs/Challenges.md)
2. Check the [list of existing tools and functionality](/docs/Tools.md)
3. See more [other tools and IDEs for inspiration](/docs/Inspirations.md)
### It's time to join the project!
:heart: Haskell tooling dream is near, we need your help! :heart:
- Register in [our google group mailing list](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/haskell-ide).
- Join [our IRC channel](https://webchat.freenode.net/?channels=haskell-ide-engine) at `#haskell-ide-engine` on `freenode`.
- Fork this repo and hack as much as you can.
- Ask @alanz or @hvr to join the project.
## Documentation
All the documentation is in [the docs folder](/docs) at the root of this project.
### Architecture
Have a look at
- the [Architecture discussion](docs/Architecture.md),
- [Protocol discussion](docs/Protocol.md) and
- [Design discussion](docs/Design.md).
## Troubleshooting
### Emacs
#### Parse errors, file state going out of sync
With the `lsp-mode` client for Emacs, it seems that the document can very easily get out of sync between, which leads to parse errors being displayed. To fix this, enable full document synchronization with
```elisp
(setq lsp-document-sync-method 'full)
```
#### [`emacs-direnv`](https://github.com/wbolster/emacs-direnv) loads environment too late
`emacs-direnv` sometimes loads the environment too late, meaning `lsp-mode` won't be able to find correct GHC/cabal versions. To fix this, add a direnv update hook *after* adding the lsp hook for `haskell-mode` (meaning the direnv hook is executed first, because hooks are LIFO):
```elisp
(add-hook 'haskell-mode-hook 'lsp)
(add-hook 'haskell-mode-hook 'direnv-update-environment)
```
### DYLD on macOS
If you hit a problem that looks like ```can't load .so/.DLL for: libiconv.dylib (dlopen(libiconv.dylib, 5): image not found)```, it means that libraries cannot be found in the library path. We can hint where to look for them and append more paths to `DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH`.
```
export DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH="$DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/lib:/usr/local/lib"
```
On practice `/usr/local/lib` is full of dylibs linked by `brew`. After you amend `DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH`, some of the previously compiled application might not work and yell about incorrect linking, for example, `dyld: Symbol not found: __cg_jpeg_resync_to_restart`. You may need to look up where it comes from and remove clashing links, in this case it were clashing images libs:
```sh
$ brew unlink libjpeg
$ brew unlink libtiff
$ brew unlink libpng
```
Recompile.
### macOS: Got error while installing GHC 8.6.1 or 8.6.2 - dyld: Library not loaded: /usr/local/opt/gmp/lib/libgmp.10.dylib
These builds have a dependency on [homebrew](https://brew.sh)'s `gmp` library. Install with brew: `brew install gmp`.
[Should be fixed in GHC 8.6.3.](https://ghc.haskell.org/trac/ghc/ticket/15769)
### macOS: Got error while processing diagnostics: unable to load package `integer-gmp-1.0.2.0`
[Rename the file](https://github.com/alanz/vscode-hie-server/issues/89#issuecomment-398212122) at `~/.stack/programs/x86_64-osx/ghc-8.4.3/lib/ghc-8.4.3/integer-gmp-1.0.2.0/HSinteger-gmp-1.0.2.0.o` to a temporary name.
[Should be fixed in GHC 8.8.1.](https://ghc.haskell.org/trac/ghc/ticket/15105)
### cannot satisfy -package-id \
#### Is \ base-x?
Make sure that the GHC version of HIE matches the one of the project. After that run
```
$ cabal configure
```
and then restart HIE (e.g. by restarting your editor).
#### Is there a hash (#) after \?
Delete any `.ghc.environment*` files in your project root and try again. (At the time of writing, cabal new-style projects are not supported with ghc-mod)
#### Otherwise
Try running `cabal update`.
### Nix: cabal-helper, No such file or directory
An error on stderr like
```
cabal-helper-wrapper: /home/<...>/.cache/cabal-helper/cabal-helper<...>: createProcess: runInteractiveProcess:
exec: does not exist (No such file or directory)
```
can happen because cabal-helper compiles and runs above executable at runtime without using nix-build, which means a Nix garbage collection can delete the paths it depends on. Delete ~/.cache/cabal-helper and restart HIE to fix this.
### Liquid Haskell
Liquid Haskell requires an SMT solver on the path. We do not take care of installing one, thus, Liquid Haskell will not run until one is installed.
The recommended SMT solver is [z3](https://github.com/Z3Prover/z3). To run the tests, it is also required to have an SMT solver on the path, otherwise the tests will fail for Liquid Haskell.
### Profiling `haskell-ide-engine`.
If you think `haskell-ide-engine` is using a lot of memory then the most useful
thing you can do is prepare a profile of the memory usage whilst you're using
the program.
1. Add `profiling: True` to the cabal.project file of `haskell-ide-engine
2. `cabal new-build hie`
3. (IMPORTANT) Add `profiling: True` to the `cabal.project` file of the project you want to profile.
4. Make a wrapper script which calls the `hie` you built in step 2 with the additional options `+RTS -hd -l-au`
5. Modify your editor settings to call this wrapper script instead of looking for `hie` on the path
6. Try using `h-i-e` as normal and then process the `*.eventlog` which will be created using `eventlog2html`.
7. Repeat the process again using different profiling options if you like.
 [![License BSD3][badge-license]][license]
[![CircleCI][badge-circleci]][circleci]
[![AppVeyor][badge-appveyor]][appveyor]
[](https://www.codetriage.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine)
[badge-license]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-BSD3-green.svg?dummy
[license]: https://github.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/blob/master/LICENSE
[badge-circleci]: https://img.shields.io/circleci/project/github/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/master.svg
[circleci]: https://circleci.com/gh/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/
[badge-appveyor]: https://ci.appveyor.com/api/projects/status/6hit7mxvgdrao3q0?svg=true
[appveyor]: https://ci.appveyor.com/project/Bubba/haskell-ide-engine-74xec
This project aims to be __the universal interface__ to __a growing number of Haskell tools__, providing a __full-featured and easy to query backend__ for editors and IDEs that require Haskell-specific functionality.
__We are currently focusing on using the [Language Server Protocol](https://github.com/Microsoft/language-server-protocol/blob/master/protocol.md) as the interface via which
we talk to clients.__
- [Haskell IDE Engine (HIE)](#haskell-ide-engine-hie)
- [Features](#features)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Installation with Nix](#installation-with-nix)
- [Installation on ArchLinux](#installation-on-archlinux)
- [Installation from source](#installation-from-source)
- [Common pre-requirements](#common-pre-requirements)
- [Linux-specific pre-requirements](#linux-specific-pre-requirements)
- [Windows-specific pre-requirements (optional)](#windows-specific-pre-requirements-optional)
- [Download the source code](#download-the-source-code)
- [Building](#building)
- [Install via cabal](#install-via-cabal)
- [Install specific GHC Version](#install-specific-ghc-version)
- [Multiple versions of HIE (optional)](#multiple-versions-of-hie-optional)
- [Configuration](#configuration)
- [Explicit Configuration](#explicit-configuration)
- [Editor Integration](#editor-integration)
- [Using HIE with VS Code](#using-hie-with-vs-code)
- [Using VS Code with Nix](#using-vs-code-with-nix)
- [Using HIE with Sublime Text](#using-hie-with-sublime-text)
- [Using HIE with Vim or Neovim](#using-hie-with-vim-or-neovim)
- [Coc](#coc)
- [LanguageClient-neovim](#languageclient-neovim)
- [vim-plug](#vim-plug)
- [Clone the LanguageClient-neovim repo](#clone-the-languageclient-neovim-repo)
- [Sample `~/.vimrc`](#sample-vimrc)
- [Using HIE with Atom](#using-hie-with-atom)
- [Using HIE with Emacs](#using-hie-with-emacs)
- [Using HIE with Spacemacs](#using-hie-with-spacemacs)
- [Using HIE with Spacemacs on Nix Based Projects](#using-hie-with-spacemacs-on-nix-based-projects)
- [Using HIE with Oni](#using-hie-with-oni)
- [Docs on hover/completion](#docs-on-hovercompletion)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [Planned Features](#planned-features)
- [It's time to join the project!](#its-time-to-join-the-project)
- [Documentation](#documentation)
- [Architecture](#architecture)
- [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting)
- [Emacs](#emacs)
- [Parse errors, file state going out of sync](#parse-errors-file-state-going-out-of-sync)
- [`emacs-direnv` loads environment too late](#emacs-direnv-loads-environment-too-late)
- [DYLD on macOS](#dyld-on-macos)
- [macOS: Got error while installing GHC 8.6.1 or 8.6.2 - dyld: Library not loaded: /usr/local/opt/gmp/lib/libgmp.10.dylib](#macos-got-error-while-installing-ghc-861-or-862---dyld-library-not-loaded-usrlocaloptgmpliblibgmp10dylib)
- [macOS: Got error while processing diagnostics: unable to load package `integer-gmp-1.0.2.0`](#macos-got-error-while-processing-diagnostics-unable-to-load-package-integer-gmp-1020)
- [cannot satisfy -package-id \
[![License BSD3][badge-license]][license]
[![CircleCI][badge-circleci]][circleci]
[![AppVeyor][badge-appveyor]][appveyor]
[](https://www.codetriage.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine)
[badge-license]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-BSD3-green.svg?dummy
[license]: https://github.com/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/blob/master/LICENSE
[badge-circleci]: https://img.shields.io/circleci/project/github/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/master.svg
[circleci]: https://circleci.com/gh/haskell/haskell-ide-engine/
[badge-appveyor]: https://ci.appveyor.com/api/projects/status/6hit7mxvgdrao3q0?svg=true
[appveyor]: https://ci.appveyor.com/project/Bubba/haskell-ide-engine-74xec
This project aims to be __the universal interface__ to __a growing number of Haskell tools__, providing a __full-featured and easy to query backend__ for editors and IDEs that require Haskell-specific functionality.
__We are currently focusing on using the [Language Server Protocol](https://github.com/Microsoft/language-server-protocol/blob/master/protocol.md) as the interface via which
we talk to clients.__
- [Haskell IDE Engine (HIE)](#haskell-ide-engine-hie)
- [Features](#features)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Installation with Nix](#installation-with-nix)
- [Installation on ArchLinux](#installation-on-archlinux)
- [Installation from source](#installation-from-source)
- [Common pre-requirements](#common-pre-requirements)
- [Linux-specific pre-requirements](#linux-specific-pre-requirements)
- [Windows-specific pre-requirements (optional)](#windows-specific-pre-requirements-optional)
- [Download the source code](#download-the-source-code)
- [Building](#building)
- [Install via cabal](#install-via-cabal)
- [Install specific GHC Version](#install-specific-ghc-version)
- [Multiple versions of HIE (optional)](#multiple-versions-of-hie-optional)
- [Configuration](#configuration)
- [Explicit Configuration](#explicit-configuration)
- [Editor Integration](#editor-integration)
- [Using HIE with VS Code](#using-hie-with-vs-code)
- [Using VS Code with Nix](#using-vs-code-with-nix)
- [Using HIE with Sublime Text](#using-hie-with-sublime-text)
- [Using HIE with Vim or Neovim](#using-hie-with-vim-or-neovim)
- [Coc](#coc)
- [LanguageClient-neovim](#languageclient-neovim)
- [vim-plug](#vim-plug)
- [Clone the LanguageClient-neovim repo](#clone-the-languageclient-neovim-repo)
- [Sample `~/.vimrc`](#sample-vimrc)
- [Using HIE with Atom](#using-hie-with-atom)
- [Using HIE with Emacs](#using-hie-with-emacs)
- [Using HIE with Spacemacs](#using-hie-with-spacemacs)
- [Using HIE with Spacemacs on Nix Based Projects](#using-hie-with-spacemacs-on-nix-based-projects)
- [Using HIE with Oni](#using-hie-with-oni)
- [Docs on hover/completion](#docs-on-hovercompletion)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [Planned Features](#planned-features)
- [It's time to join the project!](#its-time-to-join-the-project)
- [Documentation](#documentation)
- [Architecture](#architecture)
- [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting)
- [Emacs](#emacs)
- [Parse errors, file state going out of sync](#parse-errors-file-state-going-out-of-sync)
- [`emacs-direnv` loads environment too late](#emacs-direnv-loads-environment-too-late)
- [DYLD on macOS](#dyld-on-macos)
- [macOS: Got error while installing GHC 8.6.1 or 8.6.2 - dyld: Library not loaded: /usr/local/opt/gmp/lib/libgmp.10.dylib](#macos-got-error-while-installing-ghc-861-or-862---dyld-library-not-loaded-usrlocaloptgmpliblibgmp10dylib)
- [macOS: Got error while processing diagnostics: unable to load package `integer-gmp-1.0.2.0`](#macos-got-error-while-processing-diagnostics-unable-to-load-package-integer-gmp-1020)
- [cannot satisfy -package-id \