| .. | ||
| bin | ||
| example-datasets | ||
| src | ||
| test | ||
| .editorconfig | ||
| .eslintignore | ||
| .eslintrc | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| package-lock.json | ||
| package.json | ||
| README.md | ||
json2graphql: From a JSON file to postgres-backed GraphQL
json2graphql is a tool that imports a JSON file to initialise schema and data in Postgres and then allows you to start querying it with GraphQL.
Hasura is used to expose a realtime GraphQL API on Postgres. Once your schema and data is imported, you can instantly start running powerful queries with filters, pagination, sorting, fetching relations, insert/update/delete mutations and subscriptions too.
Use-cases:
- Bootstrapping a GraphQL backend: Try out this example of initialising a GraphQL chat backend using a messages/groups/users chat JSON file. Try it out
- Play with a mongo dataset in Postgres & GraphQL: Export a mongo JSON dump, import it to Postgres and start querying it with GraphQL. Try it out
- Query existing JSON datasets over GraphQL: Pick up a JSON dataset, import to your new or existing Hasura/Postgres instance and start querying it. Try using jdorfman/awesome-json-datasets.
Demo
In the GIF above, we are importing a schema and data from a JSON database. The Hasura GraphQL Engine is running at https://j2gtest.herokuapp.com
Quickstart
-
Create a JSON file Create a JSON file, say,
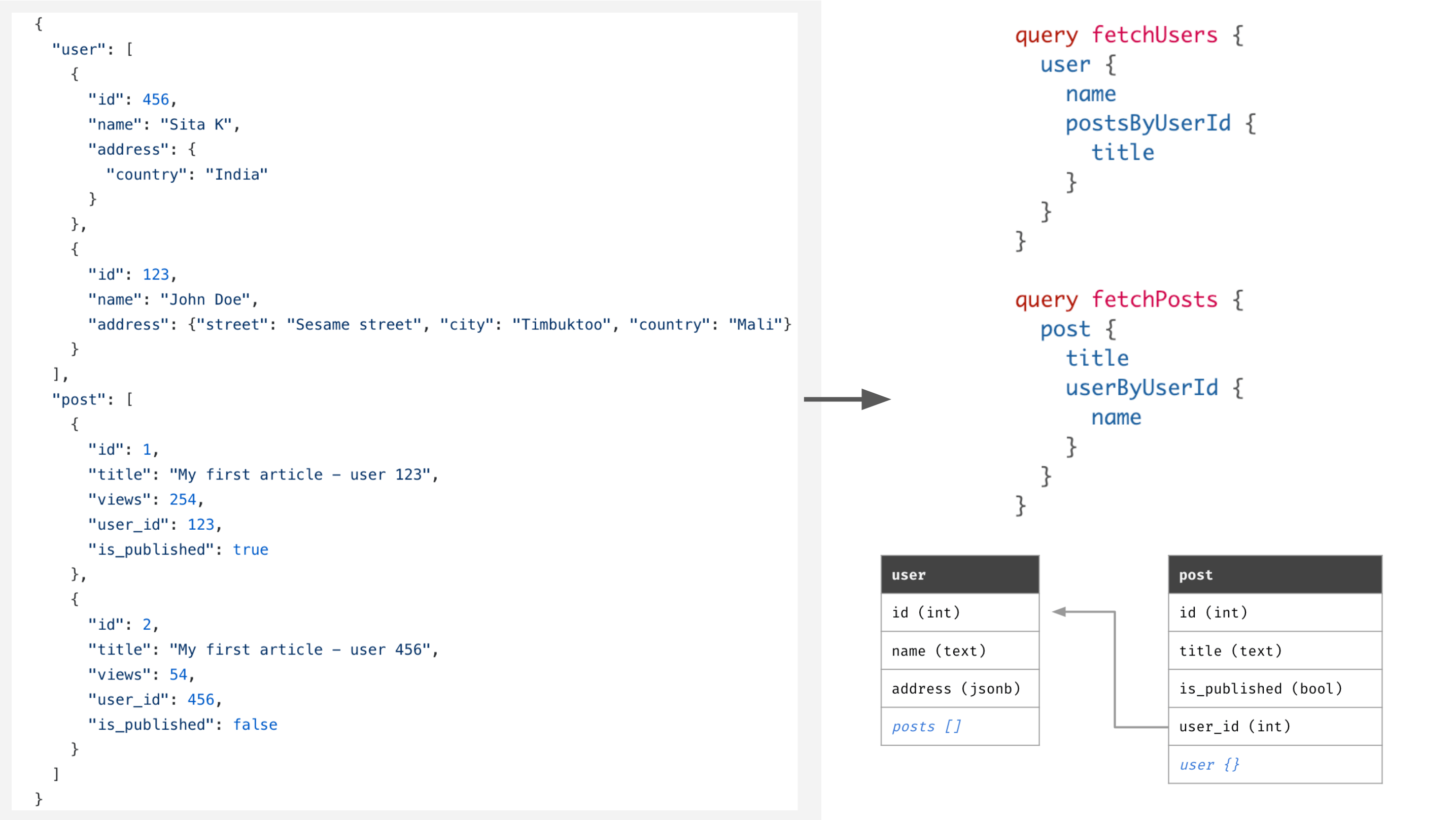
db.jsonas:{ "post": [ { "id": 1, "title": "Lorem Ipsum", "views": 254, "user_id": 123 }, { "id": 2, "title": "Sic Dolor amet", "views": 65, "user_id": 456 } ], "user": [ { "id": 123, "name": "John Doe" }, { "id": 456, "name": "Alison Craus" } ], "comment": [ { "id": 987, "post_id": 1, "body": "Consectetur adipiscing elit", "user_id": 123 }, { "id": 995, "post_id": 2, "body": "Nam molestie pellentesque dui", "user_id": 456 }, { "id": 999, "post_id": 1, "body": "quid agis", "user_id": 456 } ] } -
Run Hasura + Postgres: Run the Hasura GraphQL Engine and Postgres on Heroku's free tier by clicking this button:
Note the URL. It will be of the form:
https://<app-name>.herokuapp.com. Let's say it'sj2gtest.herokuapp.com. For instructions on how to deploy Hasura in other environments, head to the docs. -
json2graphql: We import schema, data and create Hasura configuration in one command:
npm install -g json2graphql json2graphql https://<app-name>.herokuapp.com --db=./path/to/db.json -
Run GraphQL queries: You can query the data in Postgres tables over GraphQL using Hasura GraphQL Engine. You can make complicated queries like:
query { user { postsByUserId { id title commentsByPostId { body id } } id } } -
Behind the scenes: The following schema is created in Postgres::
user ( id integer not null primary key, name text ) post ( id integer not null primary key, title text, views integer, user_id integer foreign key references user(id) ) comment ( id integer not null primary key, body text, post_id integer foreign key references post(id), user_id integer foreign key references user(id) )
Installation
## Install globally
npm install -g json2graphql
## Or run as a one-off command
npx json2graphql <hasura-url> -d ./path/to/db.json
CLI Usage
# Running against a hasura without an admin secret
json2graphql https://j2gtest.herokuapp.com -d ./path/to/db.json
# Running against a hasura with an admin secret
json2graphql https://j2gtest.herokuapp.com -s <admin-secret> -d ./path/to/db.json
# Reset configuration, schema & data and import
# Useful for updating schema structure or working against an existing Hasura setup
# WARNING: This will remove all existing schema/data before applying
json2graphql https://j2gtest.herokuapp.com --overwrite -d ./path/to/db.json
Command
json2graphql URL [flags]
Args
URL: The URL where Hasura GraphQL Engine is running
Options
-d --db: path to the JS file that exports your sample JSON database-o --overwrite: DANGER: Overwrite tables if they already exist in database-v --version: show CLI version-h, --help: show CLI help
JSON structure
The top level of your JSON database should be a JSON object with keys being the name of entities and values being list of entities. For example:
{
"user": [
{ "id": 123, "name": "John Doe" },
{ "id": 456, "name": "Jane Doe" }
],
"city": [
{ "id": 987, "name": "Stockholm", "country": "Sweden" },
{ "id": 995, "name": "Sydney", "country": "Australia" }
]
}
- The JSON structure is a "normalised" set of objects
- Top level objects are mapped to tables in postgres and root fields in the GraphQL schema
- Keys in the objects are mapped to columns of the tables in postgres, and as fields in the GraphQL schema
- Keys in the object with the column name of the form
<ENTITY_NAME>_id, are considered to indicate foreign-key constraints on postgres, and connections in the GraphQL schema - The types of the columns/fields are inferred from the data in the columns
json2graphql treats top-level objects as tables, and their keys as columns. If it encounters a column name of the form
<ENTITY_NAME>_id, json2graphql will consider it a foreign key to the entity with name<ENTITY_NAME>.
| JavaScript type (constructor.name) | Postgres column type | GraphQL field type | Example data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | numeric | numeric | 12.34 or 1223 |
| String | text | String | Hello world |
| Boolean | bool | Boolean | true |
| Date | timestamptz | timestamptz | new Date("Jan 24, 2010 00:00:00") |
| Object or Array | jsonb | jsonb | { ... } |
Generating data - importing with .js files
You can also use Javascript .js files. This allows you to:
- Write some generation logic for sample data
- Use
datetypes
module.exports = {
user: [1,2,3,4,5].map(i => ({
id: i,
name: `user-${i}`,
created: new Date()
}))
};
If you need to do some asynchronous stuff before exporting your data, you can also export an function:
Note: You can require node-fetch in your function
const fetch = require('node-fetch');
module.exports = async function() {
const db = await fetch (...)
return db
}
Use cases
Play with GraphQL on your MongoDB data
Note: This assumes that you've already run through the quickstart!
You can migrate your data from MongoDB and explore Realtime GraphQL over it.
- Tweak the MongoDB doc to fit the required JSON structure.
- Use json2graphql to import the data from the JSON
- Make realtime GraphQL queries
Consider this MongoDB doc:
-
Tweak the doc to fit the required JSON structure.
The doc originally looks something like this:
{"_id":{"$oid":"55a0f42f20a4d760b5fc305e"},"altSpellings":["AI"],"area":91, ... } {"_id":{"$oid":"55a0f42f20a4d760b5fc305e"},"altSpellings":["AI"],"area":91, ... } {"_id":{"$oid":"55a0f42f20a4d760b5fc305e"},"altSpellings":["AI"],"area":91, ... } . . .You should wrap it in an array and make the array a value of a top level key of your choice, say,
country. You should also field name_idtoidbecause the CLI expects anidfield. It should look something like this:{ "country": [ {"id":{"$oid":"55a0f42f20a4d760b5fc305e"},"altSpellings":["AI"],"area":91, ... } {"id":{"$oid":"55a0f42f20a4d760b5fc305e"},"altSpellings":["AI"],"area":91, ... } {"id":{"$oid":"55a0f42f20a4d760b5fc305e"},"altSpellings":["AI"],"area":91, ... } . . . ] } -
Use json2graphql to import the data from the JSON to Postgres using Hasura GraphQL Engine:
json2graphql https://j2gtest.herokuapp.com -d ./db.js -
Try realtime GraphQL. Go to your GraphQL Engine console and try making GraphQL queries like so:
query { country ( order_by: { name: asc } limit: 10 where: { capital: { _is_null: false }} ){ id name area currency callingCode capital } }
Quickly bootstrap a GraphQL Backend
Note: This assumes that you've already run through the quickstart!
You can write your schema and data in JSON format to quickly get a Realtime GraphQL API.
For example, to start with a group chat backend:
{
"user": [
{ "id": 1, "name": "John Doe", "username": "johndoe", "last_seen": new Date() },
{ "id": 2, "name": "Alice Wan", "username": "alisson", "last_seen": new Date() },
{ "id": 3, "name": "Natalie Jackson", "username": "nats", "last_seen": new Date() },
{ "id": 4, "name": "George Walsh", "username": "georgee", "last_seen": new Date() }
],
"group": [
{ "id": 1, "name": "Engineering", is_active: true },
{ "id": 2, "name": "Marketting", is_active: false }
],
"message": [
{ "id": 1, group_id: 1, "body": "Message 1", "sent_at": new Date(), "user_id": 1 },
{ "id": 2, group_id: 1, "body": "Message 2", "sent_at": new Date(), "user_id": 2 },
{ "id": 3, group_id: 2, "body": "Message 3", "sent_at": new Date(), "user_id": 3 },
{ "id": 4, group_id: 2, "body": "Message 4", "sent_at": new Date(), "user_id": 4 }
]
}
You can import the above JSON dataset and make queries like:
# fetch all the active groups
query fetch_groups {
group (
where: {is_active: { _eq: true }}
order_by: { name: asc }
){
id
is_active
name
}
}
# fetch all messages from a group
query fetch_messeges_from_a_group {
message(
where: { group_id: { _eq: 1 }}
order_by: { sent_at: asc }
) {
id
body
sent_at
sent_by: userByUserId {
id
username
}
}
}
Examples
For more examples, check out the ./example-datasets directory.
Credits and related projects
- Blowson and its creator Fredi Bach
- firebase2graphql: A tool to import data from firebase to a realtime GraphQL API on Postgres
- json-graphql-server