| .circleci | ||
| app | ||
| javascript | ||
| src/HaskellCodeExplorer | ||
| test | ||
| vendor/cabal-helper-0.8.1.2 | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| cabal.project | ||
| cabal.project.freeze | ||
| haskell-code-explorer.cabal | ||
| install.hs | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| Setup.hs | ||
| stack-8.0.2.yaml | ||
| stack-8.2.2.yaml | ||
| stack-8.4.3.yaml | ||
| stack-8.4.4.yaml | ||
| stack-8.6.3.yaml | ||
| stack-8.6.4.yaml | ||
| stack-8.6.5.yaml | ||
| stack-8.8.3.yaml | ||
| stack.yaml | ||
Haskell Code Explorer
Haskell Code Explorer is a web application for exploring and understanding Haskell codebases. It provides IDE-like code intelligence features such as types and documentation on hover, "go to definition", "find references" and semantic highlighting.
Examples:
- https://haskell-code-explorer.mfix.io/package/stm-2.4.5.0/show/Control/Concurrent/STM/TQueue.hs#L87
- https://haskell-code-explorer.mfix.io/package/async-2.1.1.1/show/Control/Concurrent/Async.hs#L251
- https://haskell-code-explorer.mfix.io/package/haxl-0.5.1.0/show/Haxl/Core/Monad.hs#L569
The public instance of Haskell Code Explorer is available at https://haskell-code-explorer.mfix.io. It contains core libraries (ghc, base, etc.) and a subset of packages from a Stackage snapshot.
Haskell Code Explorer consists of an indexer, an HTTP server, and a JavaScript application. The indexer uses GHC API to create a data structure that contains detailed information about the source code of a Cabal package. The HTTP server reads that data structure into memory and responds to HTTP requests from the JavaScript application.
Motivation
Reading and understanding code is an essential part of the software development process. Understanding code in any statically typed language is much easier when code intelligence features (types on hover, go-to-definition, etc.) are available. Code intelligence for Haskell is especially useful because types are informative and precise (thanks to Haskell's purity and global type inference).
Features
-
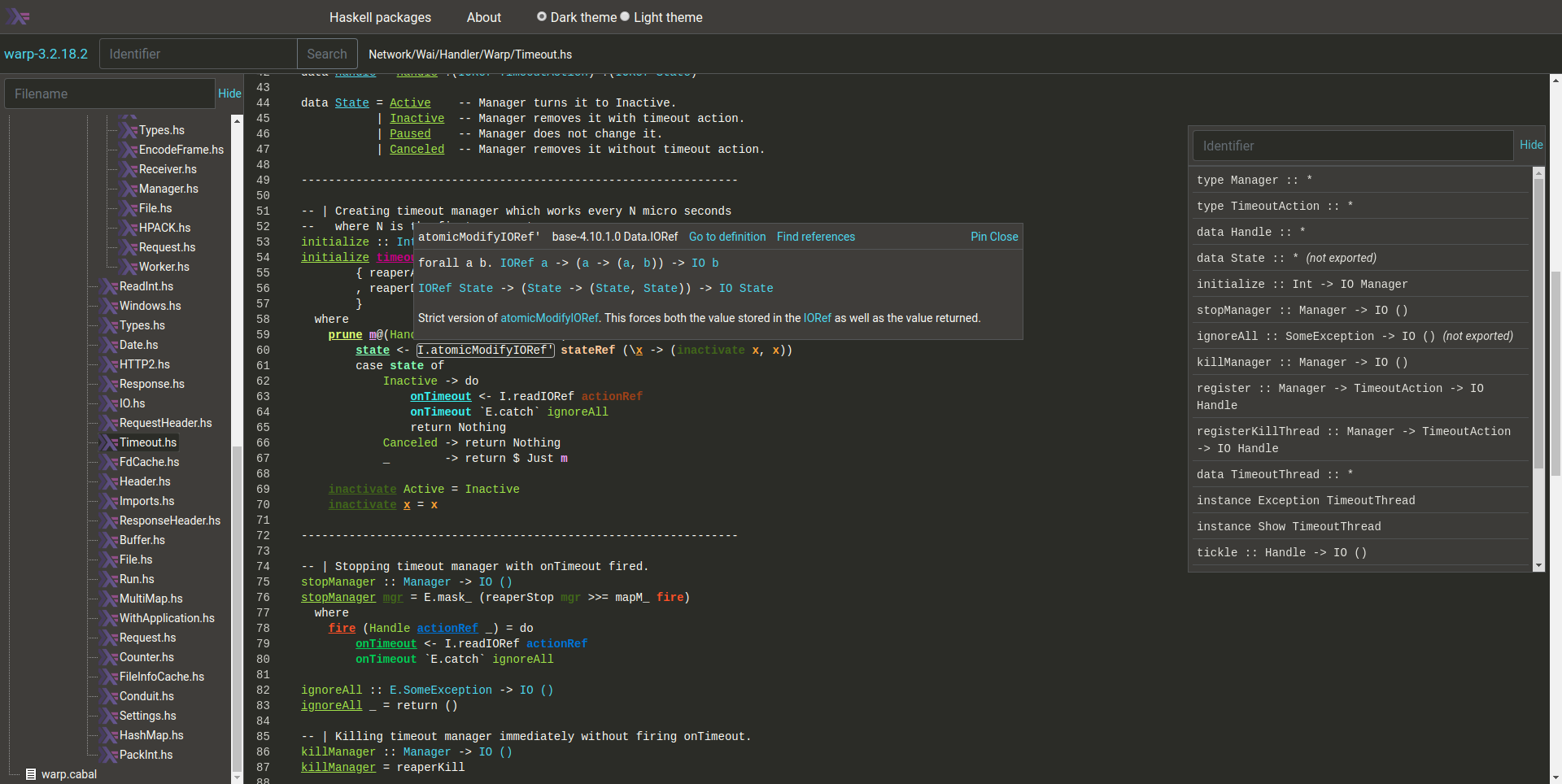
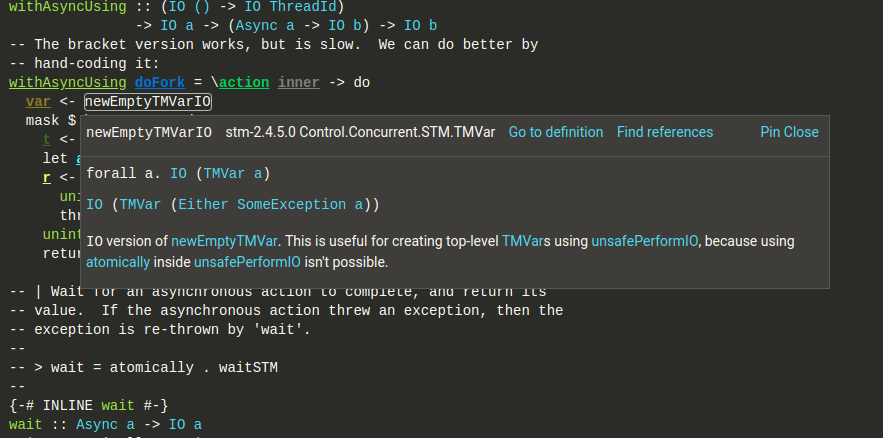
Types (actual type, instantiated type, instance resolution tree) and documentation on hover. Types are interactive: left-click on a type constructor -> go to definition, right click on a type constructor -> show kind signature.
-
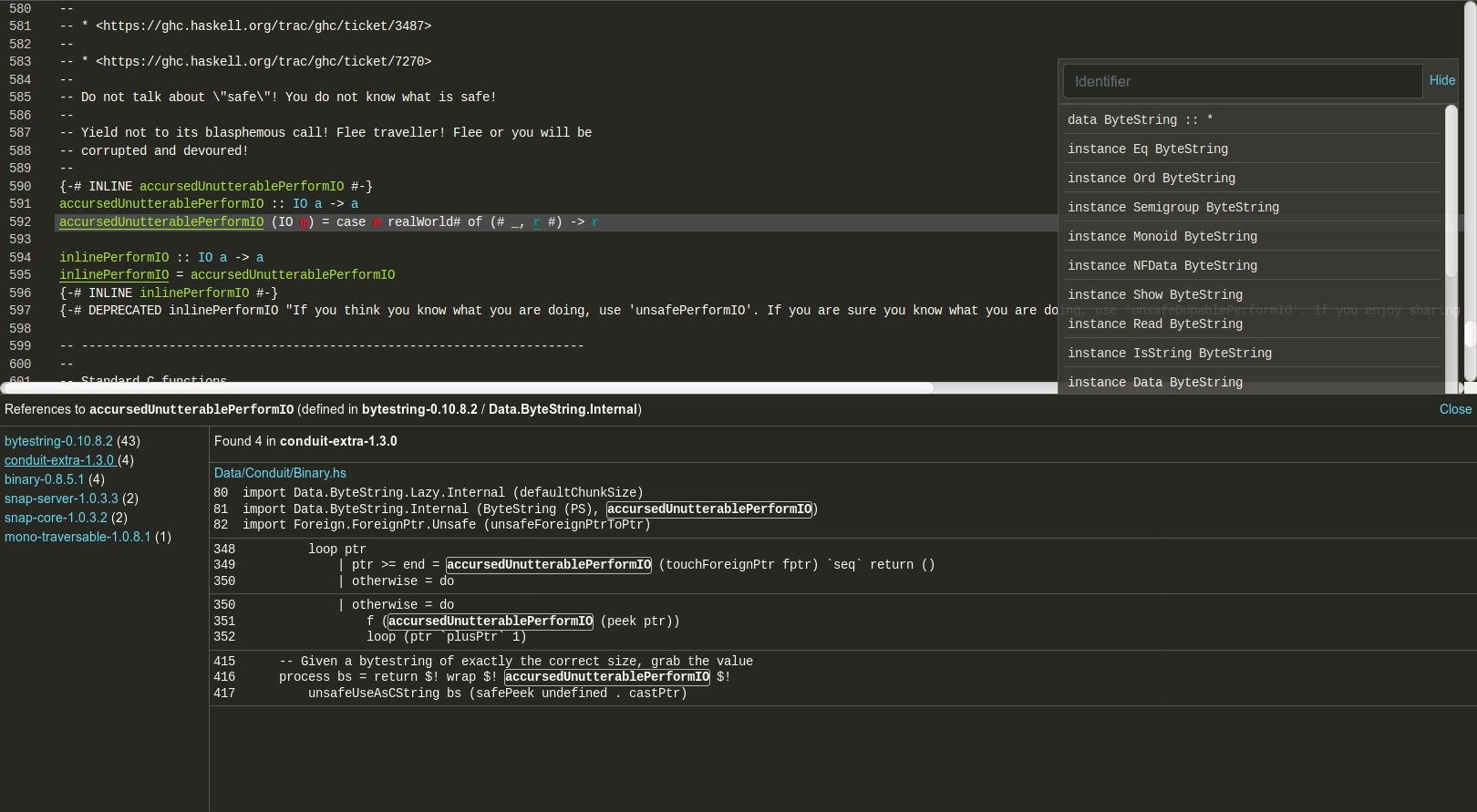
Go to definition (cross-package)
-
Search for Haskell functions, data and type constructors by name (in the current package / in all indexed packages)
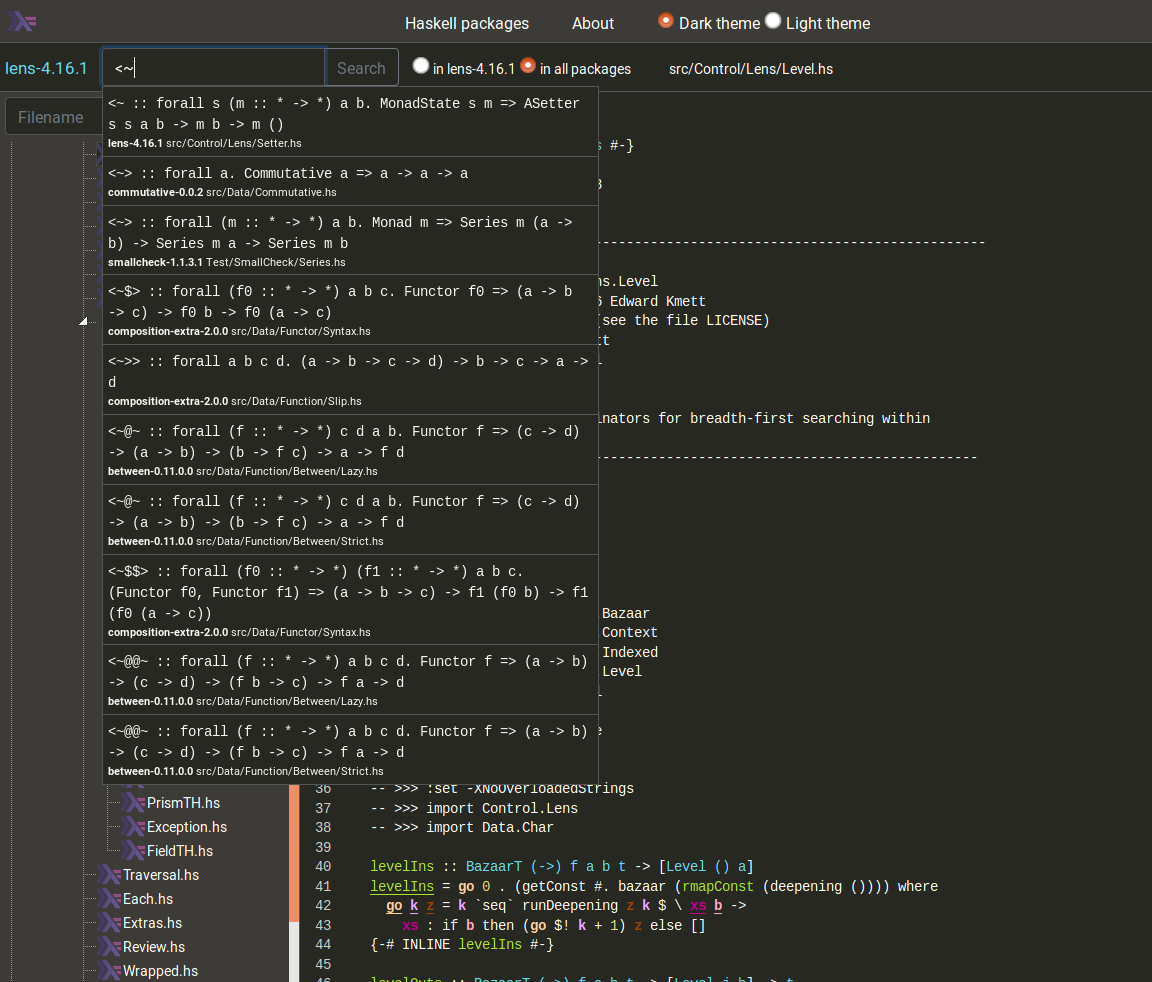
-
Type of each expression
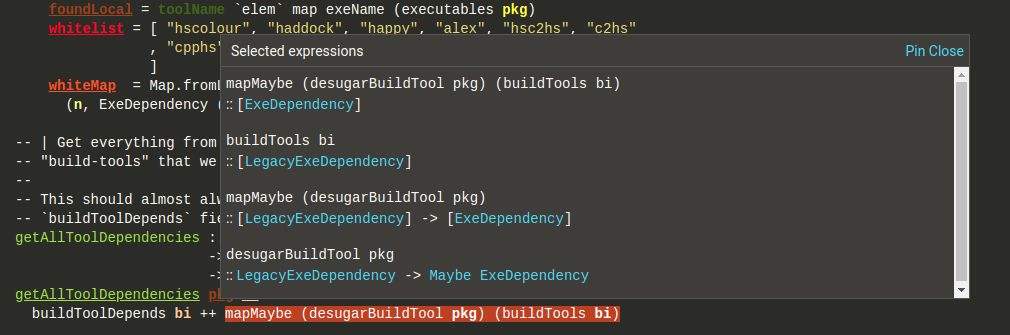
Select a piece of text to get the type of each Haskell expression inside the selection. -
Semantic highlighting
Installation
git clone https://github.com/alexwl/haskell-code-explorer
cd haskell-code-explorer
To build Haskell Code Explorer Stack (https://docs.haskellstack.org/en/stable/README/) is needed.
At the moment Haskell Code Explorer supports GHC 8.6.5, 8.6.4, GHC 8.6.3, GHC 8.4.4, GHC 8.4.3, GHC 8.2.2, and 8.0.2.
For GHC 8.6.5:
stack install
For GHC 8.6.4:
stack --stack-yaml=stack-8.6.4.yaml install
For GHC 8.6.3:
stack --stack-yaml=stack-8.6.3.yaml install
For GHC 8.4.4:
stack --stack-yaml=stack-8.4.4.yaml install
For GHC 8.4.3:
stack --stack-yaml=stack-8.4.3.yaml install
For GHC 8.2.2:
stack --stack-yaml=stack-8.2.2.yaml install
For GHC 8.0.2:
stack --stack-yaml=stack-8.0.2.yaml install
Indexing source code of a Cabal package
haskell-code-indexer executable is responsible for indexing packages (by default, the index is saved to .haskell-code-explorer directory).
A package should be built using either cabal-install or stack before indexing (cabal new-build,cabal build, or stack build command should be executed).
The version of GHC used to build haskell-code-indexer must match the version of GHC used to build a package you are indexing (to find out the version of GHC try ghc --version or stack exec ghc -- --version command).
haskell-code-indexer requires globally installed GHC and cabal-install (cabal). The reason for this is that haskell-code-indexer uses cabal-helper library https://hackage.haskell.org/package/cabal-helper to get package build information. cabal-helper builds (at runtime) an executable linked against a version of Cabal library that was used to configure the package. You may need to run cabal update to get the latest list of available packages to be able to build the cabal-helper executable. By default, the cabal-helper executable (e.g.,cabal-helper0.8.1.2-Cabal2.4.1.0) is saved to $HOME/.cache/cabal-helper.
If there is no globally installed GHC on the system, then it is possible to use stack exec command (https://docs.haskellstack.org/en/stable/GUIDE/#exec) that adds a path to GHC binaries installed by Stack to PATH environment variable.
Run cabal update using stack exec:
stack --resolver=lts-13.20 exec --no-ghc-package-path cabal -- update
Index a package using stack exec:
stack --resolver=lts-13.20 exec --no-ghc-package-path haskell-code-indexer -- INDEXER_OPTIONS
--no-ghc-package-path option unsets GHC_PACKAGE_PATH environment variable. cabal fails with the error Use of GHC's environment variable GHC_PACKAGE_PATH is incompatible with Cabal. if the GHC_PACKAGE_PATH is set.
Examples
Show all indexer options:
haskell-code-indexer -h
Index package:
haskell-code-indexer --package PATH
Index package with specific dist directory:
haskell-code-indexer --package PATH --dist dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.2.2/hpath-0.9.2
Starting HTTP Server
haskell-code-server executable reads the package index created by haskell-code-indexer and starts the HTTP server. The HTTP server responds to API requests and serves static assets (JavaScript files that are in haskell-code-explorer/javascript/release directory).
Examples
Show all server options:
haskell-code-server -h
Load the indexed package and start the server:
haskell-code-server --package PATH --port 8080
Load multiple indexed packages and start the server:
haskell-code-server --package PATH1 --package PATH2 --package PATH3 --port 8080
Load the indexed package and start the server, use Hoogle API (3dbf68bfd7/docs/API.md (json-api)) to get documentation for functions and types defined in other packages (haskell-code-server makes requests to https://hoogle.haskell.org/):
haskell-code-server --package PATH --port 8080 --use-hoogle-api
Open http://localhost:8080 in a browser to explore source code of the package.