* Wasp docs are now versioned. * Removed version 0.11.8 of docs. * Update waspc/README.md
27 KiB
Waspc
This directory contains source code of the wasp compiler (aka waspc), and this README is aimed at the contributors to the project.
If you are a Wasp user and not a contributor (yet :)), you might want to look into following resources instead (Project page, Docs).
First time contributor checklist
If you would like to make your first contribution, here is a handy checklist we made for you:
- Read Quick overview.
- Compile the project successfully and get todoApp example running (follow Basics).
- Join Discord and say hi :)!
- Pick an issue labeled with "good first issue" and let us know you would like to work on it - ideally immediatelly propose a plan of action and ask questions. If you can't find a suitable issue for you, reach out to us on Discord and we can try to find smth for you together.
- Make a PR targeting
mainand have it accepted! Check Typical workflow and Branching and merging strategy for guidance, and consult Codebase overview for more details on how Wasp compiler works internally.
Quick overview
Wasp compiler is implemented in Haskell, but you will also see a lot of Javascript and other web technologies because Wasp compiles it's own code into them.
You don't have to be expert in Haskell to contribute or understand the code, since we don't use complicated Haskell features much -> most of the code is relatively simple and straight-forward, and we are happy to help with the part that is not.
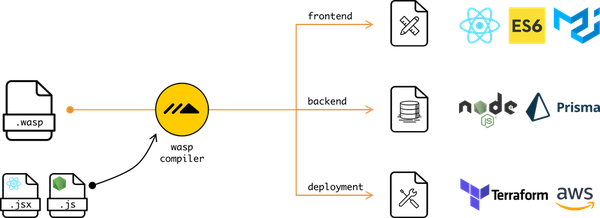
Main result of building the project is wasp executable (also reffered to as CLI), which is both Wasp compiler, CLI and Wasp project runner in one - one tool for everything Wasp-related.
wasp executable takes .wasp files and ext/ dir as input and generates a web app from them.
It can then also run that web app for you, deploy it (not yet but that is coming), and manage it in other ways.
Basics
Setup
We use the cabal command line tool to build
the project. The best way to install it is via
ghcup. The ghcup tui terminal user interface
is a convenient way of installing and selecting versions of cabal, hls and
ghc.
In cabal.project we're explicitly saying what compiler version to build Wasp with.
with-compiler: ghc-x.y.z
Ensure that you have this ghc version installed.
Repo
Fork this repo and clone the fork to your machine (or clone this repo directly if you don't plan to contribute but just want to try it out).
Position yourself in this directory (waspc/) and make sure that you are on the main branch.
Build
cabal build
to build the library and wasp executable.
This might take a while (10 mins) if you are doing it for the very first time, since cabal will need to download the external dependencies.
If that is the case, relax and feel free to get yourself a cup of coffee! When somebody asks what you are doing, you can finally rightfully say "compiling!" :D.
⚠️ You may need to run cabal update before attempting to build if it has been some time since your last update.
⚠️ If you are on Mac and get "Couldn't figure out LLVM version!" error message while building, make sure you have LLVM installed and that it is correctly exposed via env vars (PATH, LDFLAGS, CPPFLAGS). The easiest way to do it is by just running brew install llvm@13, this should install LLVM and also set up env vars in your ~/.zshrc.
Test
cabal test
to ensure all the unit and end-to-end tests are passing (this will also build the project if needed).
Executable
cabal run wasp-cli
to run the wasp-cli executable that you just built!
It should print "Usage" information.
You can pass more arguments by just adding them to the command, e.g.: cabal run wasp-cli new MyProject.
Run example app
Position yourself in waspc/examples/todoApp/ and run
cabal run wasp-cli db migrate-dev
to update database schema (this is done only on schema changes).
Then,
cabal run wasp-cli start
to run web app in development mode.
If you are doing this for the very first time, it might take a minutes or so to download and install npm dependencies.
When done, new tab in your browser should open and you will see a Todo App! NOTE: Reload page if blank.
Typical development workflow
- Create a new feature branch from
main. - If you don't have a good/reliable working HLS (Haskell Language Server) in your IDE, you will want to instead run
./run ghcidfrom the root of the project instead: this will run a process that watches the Haskell project and reports any Haskell compiler errors. Leave it running.
NOTE: You will need to installghcidglobally first. You can do it withcabal install ghcid. - Do a change in the codebase (most often in
src/orcli/src/ordata/) (together with tests if that makes sense: see "Tests"). Fix any errors shown by HLS/ghcid. Rinse and repeat. - If you did a bug fix, added new feature or did a breaking change, add short info about it to Changelog.md. Also, bump version in waspc.cabal and ChangeLog.md if needed -> check the version of latest release when doing it. If you are not sure how to decide which version to go with, check later in this file instructions on it.
- Once close to done, run
cabal testto confirm that the project's tests are passing (both new and old). - If needed, confirm that
examples/todoApp/is working correctly by runningcabal buildfirst, to build the wasp executable, and then by running that executable withcabal run wasp-cli startfrom theexamples/todoApp/dir -> this will run the web app in development mode with the current version of your Wasp code. Manually inspect that app behaves ok: In the future we will add automatic integration tests, but for now testing is manual. - Squash all the commits into a single commit (or a few in case it makes more sense) and create a PR. Keep an eye on CI tests -> they should all be passing, if not, look into it.
- If your PR changes how users(Waspers) use Wasp, make sure to also update the documentation, which is in this same repo, but under
/web/docs. - Work with reviewer(s) to get the PR approved. Keep adding "fix" commits until PR is approved, then again squash them all into one commit.
- Reviewer will merge the branch into
main. Yay!
NOTE: Why don't you use a cabal freeze file?
In order to better support a wider range of developer operating systems, we have decided against using a cabal freeze file and instead
use cabal's index-state feature to get package version pinning from hackage. See this question for more: https://github.com/haskell/cabal/issues/8059
Design docs (aka RFCs)
If the feature you are implementing is complex, be it due to its design or technical implementation, we recommend creating a design doc (aka RFC). It is a great way to share the idea you have with others while also getting help and feedback.
To create one, make a PR that adds a markdown document under wasp/docs/design-docs, and in that markdown document explain the thinking behind and choice made when deciding how to implement a feature.
Others will comment on your design doc, and once it has gone through needed iterations and is approved, you can start with the implementation of the feature (in a separate PR).
Codebase overview
Wasp is implemented in Haskell.
Codebase is split into library (src/) and CLI (which itself has a library cli/src/ and thin executable wrapper cli/exe/).
CLI is actually wasp executable, and it uses the library, where most of the logic is.
Wasp compiler takes .wasp files + everything in the ext/ dir (JS, HTML, ...) and generates a web app that consists of client, server and database.
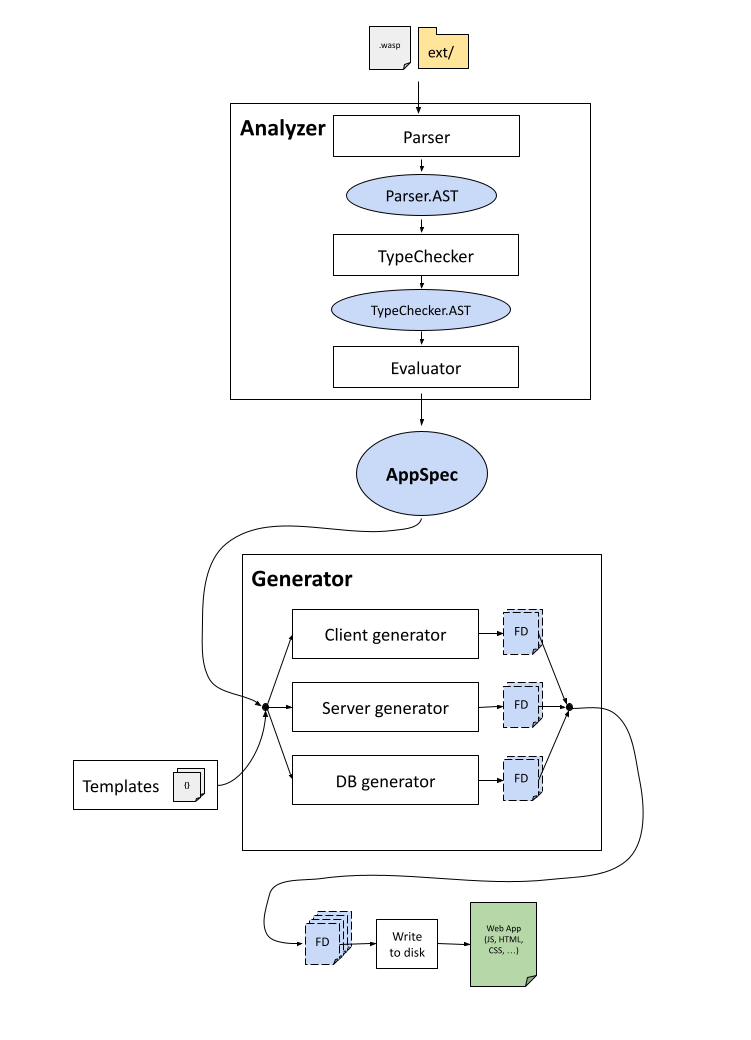
Wasp compiler code is split into 2 basic layers: Analyzer (frontend) and Generator (backend).
Wasp file(s) are analyzed by Analyzer, where they are first parsed, then typechecked, and then evaluated into a central IR (Intermediate Representation), which is AppSpec (src/Wasp/AppSpec.hs).
Check src/Wasp/Analyzer.hs for more details.
AppSpec is passed to the Generator, which based on it decides how to generate a web app.
Output of Generator is a list of FileDrafts, where each FileDraft explains how to create a file on the disk.
Therefore, Generator doesn't generate anything itself, instead it provides instructions (FileDrafts) on how to generate the web app.
FileDrafts are using mustache templates a lot (they can be found in data/Generator/templates).
Generator is split into three generators, for the three main parts of the web app: WebAppGenerator, ServerGenerator and DbGenerator.
After Generator provides us with FileDrafts, web app is generated by writing the FileDrafts to the disk.
Generated web app consists of client, server and database.
Client is written with React and react-query. Server is written in NodeJS and uses ExpressJs. Database is abstracted via Prisma.
We can run Wasp project with wasp start.
This will first compile the app, generate JS code in the .wasp/out/ dir, and then run npm start for the client, npm start for the server, and also run the database.
On any changes you do to the source code of Wasp, Wasp project gets recompiled, and then changes in the generated code are picked up by the npm start of the client/server, therefore updating the web app.
Important directories (in waspc/)
- src/ -> main source code, library
- cli/src/ -> rest of the source code, cli, uses library
- cli/exe/ -> thin executable wrapper around cli library code
- test/, e2e-test/, cli/test/ -> tests
- data/Generator/templates/ -> mustache templates for the generated client/server.
- examples/ -> example apps
Building / development (detailed)
Some useful cabal commands:
cabal updateto update your package information.cabal buildto build the project, includingwaspbinary which is both CLI and compiler in one.cabal run wasp-cli <arguments>to run thewaspbinary that was previously built.cabal testto build the whole project + tests and then also run tests.cabal install-> builds the project and places the binary so it is in PATH (so you can call it directly, from anywhere, with justwasp).
For live compilation and error checking of your code we recommend using Haskell Language Server (hls) via your IDE, but if that is not working as it should, then safe fallback is always ghcid. You can install ghcid globally with cabal install ghcid and then just type ghcid when in the project -> it will watch for any file changes and report errors.
Run script
For more convenient running of common build/dev commands, we created run script.
It mostly runs cabal commands described above, reducing the number of characters you have to type to run certain commands.
It also allows you to easily run some of the helper tools, for example tools for static analysis of our code.
The idea is that you normally use this for development, and you use cabal directly when you need more control.
It is up to you, using cabal directly is also perfectly fine and sometimes easier.
You can run ./run help to learn how to use it.
Examples:
./run ghcid-testwill run ghcid that watches tests, while passing correct arguments to ghcid../run test:unitwill run only unit tests (skipping e2e tests, which is useful since they are relatively slow)../run ormolu:formatwill format the Haskell code for you.
Tip: to make it easy to run the run script from any place in your wasp codebase, you can create a bash alias that points to it:
alias wrun="/home/martin/git/wasp-lang/wasp/waspc/run"
Typescript packages
Wasp bundles some TypeScript packages into the installation artifact (eg: deployment scripts), which end up in the installed version's waspc_datadir. To do so in CI, it runs ./tools/install_packages_to_data_dir.sh.
waspc, while implemented in Haskell, for some of its functionality on TypeScript code (e.g. for parsing TS code, or for deployment scripts). In these cases, the Haskell code runs these TS packages as separate processes and communicates through input/output streams. These packages are located in packages/ and are normal npm projects. See packages/README.md for how the projects are expected to be set up.
To make these packages available to waspc in development, run ./run wasp-packages:compile. When any changes are made to these packages, run the same command again.
Tests
For tests we are using Tasty testing framework. Tasty let's us combine different types of tests into a single test suite.
In Tasty, there is a main test file that is run when test suite is run. In that file we need to manually compose test tree out of tests that we wrote. We organize tests in test groups, which are then recursively grouped resulting in a test tree. Cool thing is that we can organize tests this way however we want and also mix different type of tests (hspec, quickcheck, and whatever else we want).
Tests are normally split in files of course, so we need to import those all the way up to the main test file, however we organize our test groups/trees.
In order to avoid need for manual organization and importing of test files described above, we are using tasty-discover which does this for us. It automatically detects files containing tests and organizes them for us into a test tree (and also takes care of importing). This means we only need to create a file, write tests in it and that is it. Test functions however do need to be prefixed with special prefix to indicate which type of test are they: spec_ for Hspec, prop_ for QuickCheck and similar. Check docs for more details. We can however still organize tests manually if we want in Tasty test trees, and then we just prefix them with test_ and tasty-discover will pick them up from there.
Additionally, currently we limited tasty-discover to auto-detect only files ending with Test.hs (*Test.hs glob). We might remove that requirement in the future if it proves to have no benefit.
To summarize: If you are writing new tests, just put them in a file that ends with Test.hs in test/ dir and that is it.
For unit testing, we use Hspec.
For property testing, we use Quickcheck.
We additionally use doctest for testing code examples in documentation.
All tests go into test/ directory.
This is convention for Haskell, opposite to mixing them with source code as in Javascript for example.
Not only that, but Haskell build tools don't have a good support for mixing them with source files, so even if we wanted to do that it is just not worth the hassle.
Tests are run with cabal test. They include both unit tests, and end-to-end tests of basic CLI commands.
To run unit tests only, you can do cabal test waspc-test (or ./run test:unit).
To run individual unit test, you can do cabal test waspc-test --test-options "-p \"Some test description to match\"" (or just ./run test:unit "Some test description to match").
To run cli tests only, you can do cabal test cli-test (or ./run test:cli).
To run end-to-end tests only, you can do cabal test e2e-test (or /run test:e2e).
End-to-end (e2e) tests
Besides unit tests, we have e2e tests that run waspc on a couple of prepared projects, check that they successfully run, and also compare generated code with the expected generated code (golden output).
This means that when you make a change in your code that modifies the generated code, e2e tests will fail while showing a diff between the new generated code and the previous (golden) one.
This gives you an opportunity to observe these differences and ensure that they are intentional and that you are satisfied with them. If you notice something unexpected or weird, you have an opportunity to fix it.
Once you are indeed happy with the changes in the generated code, you will want to update the golden output to the new (current) output, so that tests pass. Basically, you want to say "I am ok with the changes and I accept them as the new state of things.".
Easiest way to do this is to go to e2e-test/test-outputs/ dir, delete all the directories ending with -golden/, and then re-run e2e tests -> since there are no golden outputs, the new outputs will be used as new golden outputs and that is it. After that you commit that to git and you are done.
Instead of doing this manually, you can also use convenient command from the ./run script:
./run test:e2e:accept-all
Code analysis
To run the code analysis, run:
./run code-check
This will check if code is correctly formatted, if it satisfies linter, and if it passes static analysis.
These same checks are required to pass the CI, so make sure this is passing before making a PR. TODO: For now we check only the code formatting during the CI. In the future, once we make sure all the warnings are passing, we will also check linter and static analysis during the CI, but that is not happening yet.
Formatting
For formatting Haskell code we use Ormolu.
Normally we set it up in our editors to run on file save.
You can also run it manually with
./run ormolu:check
to see if there is any formatting that needs to be fixed, or with
./run ormolu:format
to have Ormolu actually format (in-place) all files that need formatting.
NOTE: When you run it for the first time it might take a while (~10 minutes) for all the dependencies to get installed. The subsequent runs will be much faster.
Linting
We use hlint for linting our Haskell code.
You can use
./run hlint
to run the hlint on Wasp codebase.
NOTE: When you run it for the first time it might take a while (~10 minutes) for all the dependencies to get installed. The subsequent runs will be much faster.
Static Analysis
We use stan to statically analyze our codebase.
The easiest way to run it is to use
./run stan
This will build the codebase, run stan on it (while installing it first, if needed, with the correct version of GHC) and then write results to the CLI and also generate report in the stan.html.
NOTE: When you run it for the first time it might take a while (~10 minutes) for all the dependencies to get installed. The subsequent runs will be much faster.
Commit message conventions
We use Conventional Commits convention when creating commits.
Branching and merging strategy
This repo contains both the source code that makes up a Wasp release (under waspc), as well as our website containing documentation and blog posts (under web). In order to facilitate the development of Wasp code while still allowing for website updates or hotfixes of the current release, we have decided on the following minimal branching strategy.
All Wasp development should be done on feature branches. They form the basis of PRs that will target one of the two following branches:
main: this branch contains all the actively developed new features and corresponding documentation updates. Some of these things may not yet be released, but anything merged intomainshould be in a release-ready state.- This is the default branch to target for any Wasp feature branches.
release: this branch contains the source code of current/latest Wasp release, as well as the documentation and blog posts currently published and therefore visible on the website.- When doing a full release, which means making a new release based on what we have currently on
main, we do the following:- Update
mainbranch by mergingreleaseinto it. There might be conflicts but they shouldn't be too hard to fix. Oncemainis updated, you can create a new waspc release from it, as well as deploy the website from it. - Update
releasebranch to this newmainby mergingmaininto it. There will be no conflicts since we already resolved all of them in the previous step.
- Update
- When doing a full release, which means making a new release based on what we have currently on
How do I know where I want to target my PR, to release or main?
- If you have a change that you want to publish right now or very soon, certainly earlier than waiting till
mainis ready for publishing, then you want to targetrelease. This could be website content update, new blog post, documentation (hot)fix, compiler hotfix that we need to release quickly via a new patch version, ... . - If you have a change that is not urgent and can wait until the next "normal" Wasp release is published, then target
main. These are new features, refactorings, docs accompanying new features, ... . - TLDR;
releaseis for changes to the already published stuff (the present).mainis for changes to the to-be-published stuff (the future).
Deployment / CI
We use Github Actions for CI.
CI runs for any commits on main branch, for pull requests, and for any commits tagged with tag that starts with v.
During CI, we build and test Wasp code on Linux, MacOS and Windows.
If commit is tagged with tag starting with v, github draft release is created from it containing binary packages.
If you put [skip ci] in commit message, that commit will be ignored by Github Actions.
We also wrote a new-release script which you can use to help you with creating new release: you need to provide it with new version (./new-release 0.3.0) and it will check that everything is all right, create appropriate tag and push it, therefore triggering CI to create new release on Github.
NOTE: If building of your commit is suddenly taking much longer time, it might be connected with cache on Github Actions. If it happens just once every so it is probably nothing to worry about. If it happens consistently, we should look into it.
Typical Release Process
- Ensure that all starter templates in
starterrepo are working with the version of Wasp we are about to release and upgrade their version of Wasp to the new one. - ChangeLog.md and version in waspc.cabal should already be up to date, but double check that they are correct and update them if needed. Also consider enriching and polishing ChangeLog.md a bit even if all the data is already there. Also check that ChangeLog has correction version of wasp specified.
- If you modified ChangeLog.md or waspc.cabal, create a PR, wait for approval and all the checks (CI) to pass, then squash and merge mentioned PR into
main. - Update your local repository state to have all remote changes (
git fetch). - Update
mainto contain changes fromreleaseby runninggit merge releasewhile on themainbranch. Resolve any conflicts. - Take a versioned "snapshot" of the current docs by running
npm run docusaurus docs:version {version}in the web dir. Check the README in thewebdir for more details. Commit this change tomain. - Fast-forward
releaseto this new, updatedmainby runninggit merge mainwhile on thereleasebranch. - Make sure you are on
releaseand then run./new-release 0.x.y.z.- This will do some checks, tag it with new release version, and push it.
- Wait for CI to finish & succeed for the new tag.
- This will automatically create a new draft release.
- Find new draft release here: https://github.com/wasp-lang/wasp/releases and edit it with your release notes.
- Publish the draft release when ready.
- Merge
releaseback intomain(git merge releasewhile on themainbranch), if needed. - Publish new docs from the
releasebranch as well. - Announce new release in Discord.
Determining next version
waspc is following typical SemVer versioning scheme, so major.minor.patch.
There is one slightly peculiar thing though: waspc, besides being a wasp compiler and CLI, also contains wasp language server (waspls) inside it, under the subcommand wasp waspls.
So how do changes to waspls affect the version of waspc, since they are packaged together as one exe? We have decided, for practical reasons, to have them affect the patch number, possibly maybe minor, but not major.
Test releases (e.g. Release Candidate)
Making a test release, especially "Release Candidate" release is useful when you want to test the release without it being published to the normal users. If doing this, steps are the following:
- You can do it from whatever branch you want, probably you will be doing it from
main. - You will want to use a version name that indicates you are doing test, probably you will want to add
-rcat the end. So for example:./new-release 0.7.0-rc. Release script will throw some warnings which you should accept. - Once draft release is created on Github, you should mark it in their UI as pre-release and publish it. This will automatically remove the checkmark from "latest release", which is exactly what we want. This is the crucial step that differentiates test release from the proper release.
- Since our wasp installer by default installs the latest release from Github, it will skip this release we made, because it is pre-release, which is great, it is what we wanted. Instead, you can install it by using the
-vflag of wasp installer! That way user's don't get in touch with it, but we can install and use it normally.
Documentation
External documentation, for users of Wasp, is hosted at https://wasp-lang.dev/docs, and its source is available at web/docs, next to the website and blog.
Make sure to update it when changes modify how Wasp works.
Haskell
We are documenting best practices related to Haskell in our Haskell Handbook.
Code style guide
General
Comments
Grammar
When writing a comment, we prefer starting it with a capital letter.
If it starts with a capital letter, it must end with a punctuation.
If it doesn't start with a capital letter, it shouldn't end with a punctuation.
TODO / NOTE
When writing a TODO or NOTE, use all capital letters, like this:
-- TODO: Wash the car.
-- NOTE: This piece of code is slow.
If you wish, you can add your name to TODO / NOTE. This is useful if you think there is a fair chance that reader of that TODO / NOTE might want to consult with its author. You can do it like this:
-- TODO(martin): Doesn't work on my machine in some unusual use cases.
JavaScript
Functions
For detailed reasoning/discussion on all listed rules, check Issue #487.
Top-level named functions
When defining top-level named functions, we prefer to use statements:
// good
function foo(param) {
// ...
}
// bad
const foo = (param) => {
// ...
}
// bad
const foo = function (param) {
// ...
}
Inline function expression
When defining inline function expressions, we prefer the arrow syntax:
// good
const squares = arr.map(x => x * x)
// bad
const squares = arr.map(function (x) { return x * x })